Moderate blast exposure results in increased IL-6 and TNFα in peripheral blood
- PMID: 28232173
- PMCID: PMC5537025
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.02.015
Moderate blast exposure results in increased IL-6 and TNFα in peripheral blood
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Moderate blast exposure results in increased IL-6 and TNFa in peripheral blood" [Brain Behav. Immun. 65 (2017) 90-94].Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Mar;69:631. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.11.021. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 29249637 No abstract available.
Abstract
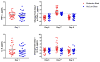
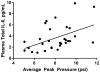
A unique cohort of military personnel exposed to isolated blast was studied to explore acute peripheral cytokine levels, with the aim of identifying blast-specific biomarkers. Several cytokines, including interleukin (IL) 6, IL-10 and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) have been linked to pre-clinical blast exposure, but remained unstudied in clinical blast exposure. To address this gap, blood samples from 62 military personnel were obtained at baseline, and daily, during a 10-day blast-related training program; changes in the peripheral concentrations of IL-6, IL-10 and TNFα were evaluated using an ultrasensitive assay. Two groups of trainees were matched on age, duration of military service, and previous history of blast exposure(s), resulting in moderate blast cases and no/low blast controls. Blast exposures were measured using helmet sensors that determined the average peak pressure in pounds per square inch (psi). Moderate blast cases had significantly elevated concentrations of IL-6 (F1,60=18.81, p<0.01) and TNFα (F1,60=12.03, p<0.01) compared to no/low blast controls; levels rebounded to baseline levels the day after blast. On the day of the moderate blast exposure, the extent of the overpressure (psi) in those exposed correlated with IL-6 (r=0.46, p<0.05) concentrations. These findings indicate that moderate primary blast exposure results in changes, specifically acute and transient increases in peripheral inflammatory markers which may have implications for neuronal health.
Keywords: Blast; Cytokines; Inflammation; Military; Traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Altara R, Manca M, Hermans KC, Daskalopoulos EP, Brunner-La Rocca HP, Hermans RJ, Struijker-Boudier HA, Blankesteijn MW. Diurnal rhythms of serum and plasma cytokine profiles in healthy elderly individuals assessed using membrane based multiplexed immunoassay. J Transl Med. 2015;13:129. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Black PH. Stress and the inflammatory response: a review of neurogenic inflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 2002;16:622–653. - PubMed
-
- Carr W, Stone JR, Walilko T, Young LA, Snook TL, Paggi ME, Tsao JW, Jankosky CJ, Parish RV, Ahlers ST. Repeated Low-Level Blast Exposure: A Descriptive Human Subjects Study. Military medicine. 2016;181:28–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

