Effect of Race and Ethnicity on Antihypertensive Medication Utilization Among Women in the United States: Study of Women's Health Across the Nation (SWAN)
- PMID: 28232324
- PMCID: PMC5524010
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004758
Effect of Race and Ethnicity on Antihypertensive Medication Utilization Among Women in the United States: Study of Women's Health Across the Nation (SWAN)
Abstract
Background: Antihypertensive medication use may vary by race and ethnicity. Longitudinal antihypertensive medication use patterns are not well described in women.
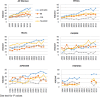
Methods and results: Participants from the Study of Women's Health Across the Nation (SWAN), a prospective cohort of women (n=3302, aged 42-52), who reported a diagnosis of hypertension or antihypertensive medication use at any annual visit were included. Antihypertensive medications were grouped by class and examined by race/ethnicity adjusting for potential confounders in logistic regression models. A total of 1707 (51.7%) women, mean age 50.6 years, reported hypertension or used antihypertensive medications at baseline or during follow-up (mean 9.1 years). Compared with whites, blacks were almost 3 times as likely to receive a calcium channel blocker (odds ratio, 2.92; 95% CI, 2.24-3.82) and twice as likely to receive a thiazide diuretic (odds ratio, 2.38; 95% CI, 1.93-2.94). Blacks also had a higher probability of reporting use of ≥2 antihypertensive medications (odds ratio, 1.95; 95% CI, 1.55-2.45) compared with whites. Use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers and thiazide diuretics increased over time for all racial/ethnic groups. Contrary to our hypothesis, rates of β-blocker usage did not decrease over time.
Conclusions: Among this large cohort of multiethnic midlife women, use of antihypertensive medications increased over time, with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers becoming the most commonly used antihypertensive medication, even for blacks. Thiazide diuretic utilization increased over time for all race/ethnic groups as did use of calcium channel blockers among blacks; both patterns are in line with guideline recommendations for the management of hypertension.
Keywords: disparities; hypertension; medication; race/ethnicity; women.
© 2017 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Temporal patterns of antihypertensive medication use among elderly patients. The Cardiovascular Health Study.JAMA. 1993 Oct 20;270(15):1837-41. JAMA. 1993. PMID: 8105112
-
Association between cardiovascular outcomes and antihypertensive drug treatment in older women.JAMA. 2004 Dec 15;292(23):2849-59. doi: 10.1001/jama.292.23.2849. JAMA. 2004. PMID: 15598916
-
Racial/ethnic disparities in medication use among veterans with hypertension and dementia: a national cohort study.Ann Pharmacother. 2009 Feb;43(2):185-93. doi: 10.1345/aph.1L368. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Ann Pharmacother. 2009. PMID: 19193586
-
Hypertension and ethnicity.Curr Opin Cardiol. 2016 Jul;31(4):381-6. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000293. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27137760 Review.
-
The impact of ethnicity on response to antihypertensive therapy.Am J Med. 1996 Sep 30;101(3A):22S-32S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(96)00265-3. Am J Med. 1996. PMID: 8876472 Review.
Cited by
-
Physiologic and psychosocial changes of the menopause transition in US Latinas: a narrative review.Climacteric. 2021 Jun;24(3):214-228. doi: 10.1080/13697137.2020.1834529. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Climacteric. 2021. PMID: 33174466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Despres JP, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Isasi CR, Jimenez MC, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Liu S, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, McGuire DK, Mohler ER III, Moy CS, Muntner P, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Rodriguez CJ, Rosamond W, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Woo D, Yeh RW, Turner MB; American Heart Association Statistics C and Stroke Statistics S . Heart disease and stroke statistics—2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133:e38–e360. - PubMed
-
- Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd‐Jones DM, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Makuc DM, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, Moy CS, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino ME, Nichol G, Paynter NP, Soliman EZ, Sorlie PD, Sotoodehnia N, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2012 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2012;125:e2–e220. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Franco OH, Peeters A, Bonneux L, de Laet C. Blood pressure in adulthood and life expectancy with cardiovascular disease in men and women: life course analysis. Hypertension. 2005;46:280–286. - PubMed
-
- Ferdinand KC, Ferdinand DP. Race‐based therapy for hypertension: possible benefits and potential pitfalls. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2008;6:1357–1366. - PubMed
-
- Hertz RP, Unger AN, Cornell JA, Saunders E. Racial disparities in hypertension prevalence, awareness, and management. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:2098–2104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

