Late effects of blood and marrow transplantation
- PMID: 28232372
- PMCID: PMC5395102
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2016.150250
Late effects of blood and marrow transplantation
Abstract
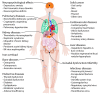
Hematopoietic cell transplantation is a curative treatment for a variety of hematologic diseases. Advances in transplantation technology have reduced early transplant-related mortality and expanded application of transplantation to older patients and to a wider variety of diseases. Management of late effects after transplantation is increasingly important for a growing number of long-term survivors that is estimated to be half a million worldwide. Many studies have shown that transplant survivors suffer from significant late effects that adversely affect morbidity, mortality, working status and quality of life. Late effects include diseases of the cardiovascular, pulmonary, and endocrine systems, dysfunction of the thyroid gland, gonads, liver and kidneys, infertility, iron overload, bone diseases, infection, solid cancer, and neuropsychological effects. The leading causes of late mortality include recurrent malignancy, lung diseases, infection, secondary cancers and chronic graft-versus-host disease. The aim of this review is to facilitate better care of adult transplant survivors by summarizing accumulated evidence, new insights, and practical information about individual late effects. Further research is needed to understand the biology of late effects allowing better prevention and treatment strategies to be developed.
Copyright© Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures
Comment in
-
Late effects of blood and marrow transplantation.Haematologica. 2017 Nov;102(11):e465. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.176289. Haematologica. 2017. PMID: 29079647 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Thomas E, Storb R, Clift RA, et al. Bone-marrow transplantation (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975;292(16):832–843. - PubMed
-
- Gluckman E, Rocha V, Boyer-Chammard A, et al. Outcome of cord-blood transplantation from related and unrelated donors. Eurocord Transplant Group and the European Blood and Marrow Transplantation Group. N Engl J Med. 1997;337(6):373–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical