A complex of Arabidopsis DRB proteins can impair dsRNA processing
- PMID: 28232389
- PMCID: PMC5393186
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.059519.116
A complex of Arabidopsis DRB proteins can impair dsRNA processing
Abstract
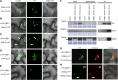
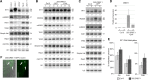
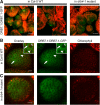
Small RNAs play an important role in regulating gene expression through transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene silencing. Biogenesis of small RNAs from longer double-stranded (ds) RNA requires the activity of dicer-like ribonucleases (DCLs), which in plants are aided by dsRNA binding proteins (DRBs). To gain insight into this pathway in the model plant Arabidopsis, we searched for interactors of DRB4 by immunoprecipitation followed by mass spectrometry-based fingerprinting and discovered DRB7.1. This interaction, verified by reciprocal coimmunoprecipitation and bimolecular fluorescence complementation, colocalizes with markers of cytoplasmic siRNA bodies and nuclear dicing bodies. In vitro experiments using tobacco BY-2 cell lysate (BYL) revealed that the complex of DRB7.1/DRB4 impairs cleavage of diverse dsRNA substrates into 24-nucleotide (nt) small interfering (si) RNAs, an action performed by DCL3. DRB7.1 also negates the action of DRB4 in enhancing accumulation of 21-nt siRNAs produced by DCL4. Overexpression of DRB7.1 in Arabidopsis altered accumulation of siRNAs in a manner reminiscent of drb4 mutant plants, suggesting that DRB7.1 can antagonize the function of DRB4 in siRNA accumulation in vivo as well as in vitro. Specifically, enhanced accumulation of siRNAs from an endogenous inverted repeat correlated with enhanced DNA methylation, suggesting a biological impact for DRB7.1 in regulating epigenetic marks. We further demonstrate that RNase three-like (RTL) proteins RTL1 and RTL2 cleave dsRNA when expressed in BYL, and that this activity is impaired by DRB7.1/DRB4. Investigating the DRB7.1-DRB4 interaction thus revealed that a complex of DRB proteins can antagonize, rather than promote, RNase III activity and production of siRNAs in plants.
Keywords: DCL; RNA silencing; RNase III; RNase three-like; double-stranded RNA binding protein (DRB); endogenous inverted repeats; in vitro BY-2 lysate.
© 2017 Tschopp et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A specific dsRNA-binding protein complex selectively sequesters endogenous inverted-repeat siRNA precursors and inhibits their processing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Feb 17;45(3):1330-1344. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1264. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28180322 Free PMC article.
-
NMR resonance assignments of 18.5 kDa complex of Arabidopsis thaliana DRB7.2:DRB4 interaction domains.Biomol NMR Assign. 2023 Dec;17(2):173-178. doi: 10.1007/s12104-023-10137-3. Epub 2023 May 31. Biomol NMR Assign. 2023. PMID: 37256435
-
Arabidopsis double-stranded RNA binding protein DRB3 participates in methylation-mediated defense against geminiviruses.J Virol. 2014 Mar;88(5):2611-22. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02305-13. Epub 2013 Dec 18. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24352449 Free PMC article.
-
Plant dicer-like proteins: double-stranded RNA-cleaving enzymes for small RNA biogenesis.J Plant Res. 2017 Jan;130(1):33-44. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0877-1. Epub 2016 Nov 24. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 27885504 Review.
-
Structural basis for non-catalytic and catalytic activities of ribonuclease III.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006 Aug;62(Pt 8):933-40. doi: 10.1107/S090744490601153X. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006. PMID: 16855311 Review.
Cited by
-
A Glimpse of "Dicer Biology" Through the Structural and Functional Perspective.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 7;8:643657. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.643657. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34026825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plastidial NAD-Dependent Malate Dehydrogenase: A Moonlighting Protein Involved in Early Chloroplast Development through Its Interaction with an FtsH12-FtsHi Protease Complex.Plant Cell. 2018 Aug;30(8):1745-1769. doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00121. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Plant Cell. 2018. PMID: 29934433 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of SlDRB1 gene reduces resistance to tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum).Plant Signal Behav. 2022 Dec 31;17(1):2149942. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2022.2149942. Plant Signal Behav. 2022. PMID: 36453197 Free PMC article.
-
LIKE SEX4 1 Acts as a β-Amylase-Binding Scaffold on Starch Granules during Starch Degradation.Plant Cell. 2019 Sep;31(9):2169-2186. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00089. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Plant Cell. 2019. PMID: 31266901 Free PMC article.
-
A new level of RNA-based plant protection: dsRNAs designed from functionally characterized siRNAs highly effective against Cucumber mosaic virus.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 27;53(5):gkaf136. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf136. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40103224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adenot X, Elmayan T, Lauressergues D, Boutet S, Bouché N, Gasciolli V, Vaucheret H. 2006. DRB4-dependent TAS3 trans-acting siRNAs control leaf morphology through AGO7. Curr Biol 16: 927–932. - PubMed
-
- Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Sung GH, Spatafora JW, Carrington JC. 2004. Evolution of microRNA genes by inverted duplication of target gene sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 36: 1282–1290. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. 2001. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409: 363–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
