Global diversity and molecular systematics of Wrightoporia s.l. (Russulales, Basidiomycota)
- PMID: 28232759
- PMCID: PMC5315289
- DOI: 10.3767/003158516X689666
Global diversity and molecular systematics of Wrightoporia s.l. (Russulales, Basidiomycota)
Abstract
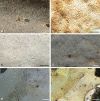
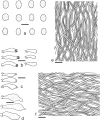
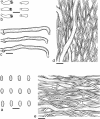
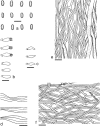
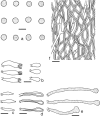
Wrightoporia accommodates polypores producing finely asperulate and amyloid basidiospores, and causing white rot. Thirty-nine species have been described or transferred to this genus; however, only a few species have been referred to molecular phylogeny. In this study, about 140 worldwide specimens of Wrightoporia s.l. were studied morphologically, and ITS and/or nLSU regions from 37 samples, representing 19 species, were sequenced for phylogenetic analysis. Six clades of Wrightoporia s.l. were recognized. The Wrightoporia s.str. clade includes W. avellanea, W. lenta (the generic type) and W. subavellanea. Three clades segregating from Wrightoporia s.str. were proposed separately as three new genera, namely Larssoniporia gen. nov., Pseudowrightoporia gen. nov. and Wrightoporiopsis gen. nov. Two other clades were named after Amylonotus and Amylosporus. According to phylogenetic and morphological evidence, species previously treated in Wrightoporia were transferred to Amylonotus, Amylosporus and the new genera, or were retained as members of Wrightoporia s.l. because no good solution for these species could be found so far. In addition, one new species in Larssoniporia, three new species in Pseudowrightoporia and two new species in Wrightoporiopsis were described. Identification keys to the six genera and species in Amylonotus, Amylosporus, Larssoniporia, Pseudowrightoporia, Wrightoporia and Wrightoporiopsis are provided, respectively.
Keywords: ITS; nLSU; polypore; wood-inhabiting fungi.
Figures




References
-
- Buchanan PK, Ryvarden L. 2000. New Zealand polypore fungi: six new species and a redetermination. New Zealand Journal of Botany 38: 251–263.
-
- Chen JJ, Cui BK. 2012. Studies on Wrightoporia from China 2. A new species and three new records from South China. Mycotaxon 21: 333–343.
-
- Chen JJ, Cui BK. 2014. Studies on Wrightoporia from China 3. Wrightoporia subavellanea sp. nov. based on morphological characters and rDNA sequence data. Phytotaxa 175: 225–234.
-
- Chen JJ, Yu HY. 2012. Studies on the genus of Wrightoporia from China 1. A new species described from Hunan Province, South China. Mycotaxon 120: 295–300.
-
- Corner EJH. 1989. Ad Polyporaceas 5. Beihefte zur Nova Hedwigia 97: 1–218.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
