N-Butylphthalide Improves Cognitive Function in Rats after Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
- PMID: 28232802
- PMCID: PMC5298996
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00064
N-Butylphthalide Improves Cognitive Function in Rats after Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Abstract
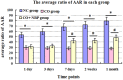
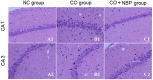
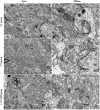
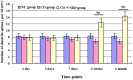
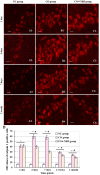
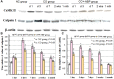
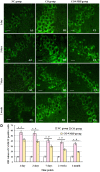
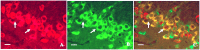
Cognitive impairment is the most common neurologic sequelae after carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning, and the previous investigations have demonstrated that N-Butylphthalide (NBP) could exert a broad spectrum of neuroprotective properties. The current study aimed to investigate the effect of NBP on cognitive dysfunction in rats after acute severe CO poisoning. Rats were randomly divided into a normal control group, a CO poisoning group and a CO+NBP group. The animal model of CO poisoning was established by exposure to CO in a chamber, and then all rats received hyperbaric oxygen therapy once daily, while rats in CO+NBP group were administered orally NBP (6 mg/ 100g) by gavage twice a day additionally. The results indicated that CO poisoning could induce cognitive impairment. The ultrastructure of hippocampus was seriously damaged under transmission electron microscopy, and the expressions of calpain 1 and CaMK II proteins were significantly elevated after CO exposure according to the analysis of immunofluorescence staining and western blot. NBP treatment could evidently improve cognitive function, and maintain ultrastructure integrity of hippocampus. The expression levels of both calpain 1 and CaMK II proteins in CO+NBP group were considerably lower than that of CO poisoning group (P < 0.05). Taken together, this study highlights the molecular mechanism of cognitive dysfunction in rats after CO exposure via the upregulation of both calpain 1 and CaMK II proteins. The administration of NBP could balance the expressions of calpain 1 and CaMK II proteins and improve cognitive function through maintaining ultrastructural integrity of hippocampus, and thus may play a neuroprotective role in brain tissue in rats with CO poisoning.
Keywords: CO poisoning; Ca2+/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II; Calpain 1; N-butylphthalide; cognitive function; rat.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evidence of clinical efficacy and pharmacological mechanism of N-butylphthalide in the treatment of delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning.Front Neurol. 2023 Mar 16;14:1119871. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1119871. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37006490 Free PMC article.
-
Application and prospects of butylphthalide for the treatment of neurologic diseases.Chin Med J (Engl). 2019 Jun 20;132(12):1467-1477. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000289. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019. PMID: 31205106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Effects of N-butylphthalide on the expressions of calpain 1 and CaMK II in hippocampus in rats with acute severe carbon monoxide poisoning].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017 Dec;29(12):1127-1132. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.12.015. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017. PMID: 29216949 Chinese.
-
[Effects of N-butylphthalide on the expressions of ZO-1 and claudin-5 in blood-brain barrier of rats with acute carbon monoxide poisoning].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 May;30(5):422-427. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.05.006. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 29764545 Chinese.
-
N-Butylphthalide Alleviates Blood-Brain Barrier Impairment in Rats Exposed to Carbon Monoxide.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Oct 26;7:394. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00394. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27833554 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Examination of central nervous system by functional observation battery after massive intravenous infusion of carbon monoxide-bound and oxygen-bound hemoglobin vesicles in rats.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022 Oct 4;3:100135. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100135. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 36568263 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of clinical efficacy and pharmacological mechanism of N-butylphthalide in the treatment of delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning.Front Neurol. 2023 Mar 16;14:1119871. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1119871. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37006490 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Cognitive Functions: a Systematic Review.Neuropsychol Rev. 2022 Mar;32(1):99-126. doi: 10.1007/s11065-021-09500-9. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Neuropsychol Rev. 2022. PMID: 33847854 Free PMC article.
-
Application and prospects of butylphthalide for the treatment of neurologic diseases.Chin Med J (Engl). 2019 Jun 20;132(12):1467-1477. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000289. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019. PMID: 31205106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hesperidin neuroprotective effects against carbon monoxide-induced toxicity in male rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Oct;397(10):7673-7681. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03132-5. Epub 2024 May 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38700797
References
-
- Chen N. C., Chang W. N., Lui C. C., Huang S. H., Lee C. C., Huang C. W., et al. (2013). Detection of gray matter damage using brain MRI and SPECT in carbon monoxide intoxication: a comparison study with neuropsychological correlation. Clin. Nucl. Med. 38 e53–e59. 10.1097/RLU.0b013e31827082a7 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

