Dysregulated Responsiveness of Circulating Dendritic Cells to Toll-Like Receptors in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis
- PMID: 28232832
- PMCID: PMC5298972
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00102
Dysregulated Responsiveness of Circulating Dendritic Cells to Toll-Like Receptors in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis
Abstract
Objective: Dendritic cells (DCs) are critical effectors of innate and adaptive immunity playing crucial roles in autoimmune responses. We previously showed that blood DC numbers were reduced in autoimmune antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitis (AAV). Here, we assessed toll-like receptor (TLR) responsiveness of blood DCs from patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) or microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
Methods: Blood samples from healthy controls (HCs), GPA, or MPA patients, without treatment, during acute phase (AP) or remission phase (RP) were analyzed. Cytokine production by DCs and T cells was assessed on whole blood by flow cytometry after TLRs or polyclonal stimulation, respectively.
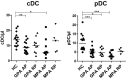
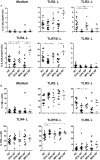
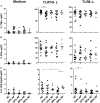
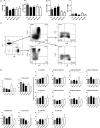
Results: We first showed that GPA and MPA are associated with a decreased blood DC number during AP. Conventional DCs (cDCs) from patients with GPA and MPA in AP exhibited a profound decrease of IL-12/IL-23p40 production after TLR3, 4, or 7/8 stimulation compared to patients in remission and HC, with a return to normal values in RP. TNFα secretion was also affected, with a decrease in cDCs from GPA patients in AP after TLR3 stimulation but an increase after TLR7/8 stimulation. By contrast, the responsiveness of plasmacytoid DCs to TLR7 and 9 was only marginally affected. Finally, we observed that IFNγ-producing CD4+ T cell frequency was significantly lower in AP-GPA patients than in HC.
Conclusion: We describe, for the first time, a dysregulated response to TLRs of circulating DCs in AAV patients mostly affecting cDCs that exhibit an unexpected reduced inflammatory cytokine secretion possibly contributing to an altered Th cell response.
Keywords: ANCA-associated vasculitis; IL-12/IL-23p40; dendritic cells; dysregulation; toll-like receptor.
Figures
References
-
- Hellmich B, Flossmann O, Gross WL, Bacon P, Cohen-Tervaert JW, Guillevin L, et al. EULAR recommendations for conducting clinical studies and/or clinical trials in systemic vasculitis: focus on anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis (2007) 66:605–17. 10.1136/ard.2006.062711 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

