Percutaneous Ventricular Assist Devices: A Health Technology Assessment
- PMID: 28232854
- PMCID: PMC5313122
Percutaneous Ventricular Assist Devices: A Health Technology Assessment
Abstract
Background: Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)-using a catheter to place a stent to keep blood vessels open-is increasingly used for high-risk patients who cannot undergo surgery. Cardiogenic shock (when the heart suddenly cannot pump enough blood) is associated with a high mortality rate. The percutaneous ventricular assist device can help control blood pressure and increase blood flow in these high-risk conditions. This health technology assessment examined the benefits, harms, and budget impact of the Impella percutaneous ventricular assist device in high-risk PCI and cardiogenic shock. We also analyzed cost-effectiveness of the Impella device in high-risk PCI.
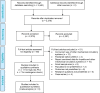
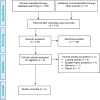
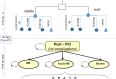
Methods: We performed a systematic search of the literature for studies examining the effects of the Impella percutaneous ventricular assist device in high-risk PCI and cardiogenic shock, and appraised the evidence according to the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) Working Group criteria, focusing on hemodynamic stability, mortality, major adverse cardiac events, bleeding, and vascular complications. We developed a Markov decision-analytical model to assess the cost- effectiveness of Impella devices versus intra-aortic balloon pumps (IABPs), calculated incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) using a 10-year time horizon, and conducted sensitivity analyses to examine the robustness of the estimates. The economic model was conducted from the perspective of the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care.
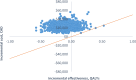
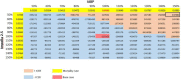
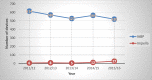
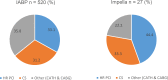
Results: Eighteen studies (one randomized controlled trial and 10 observational studies for high-risk PCI, and one randomized controlled trial and six observational studies for cardiogenic shock) were included in the clinical review. Compared with IABPs, Impella 2.5, one model of the device, improved hemodynamic parameters (GRADE low-very low) but showed no significant difference in mortality (GRADE low), major adverse cardiac events (GRADE low), bleeding (GRADE low), or vascular complications (GRADE low) in high-risk PCI and cardiogenic shock. No randomized controlled trials or prospective observational studies with a control group have studied Impella CP and Impella 5.0 (other models of the device) in patients undergoing high-risk PCI or patients with cardiogenic shock. The economic model predicted that treatment with the Impella device would have fewer quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) and higher costs than IABP in high-risk PCI patients. These observations were consistent even when uncertainty in model inputs and parameters was considered. We estimated that adopting Impella would increase costs by $2.9 to $11.5 million per year.
Conclusions: On the basis of evidence of low to very low quality, Impella 2.5 devices were associated with improved hemodynamic stability, but had mortality rates and safety profile similar to IABPs in high-risk PCI and cardiogenic shock. Our cost-effectiveness analysis indicated that Impella 2.5 is likely associated with greater costs and fewer quality-adjusted life years than IABP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Cardiac Indications in Adults: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020 Mar 6;20(8):1-121. eCollection 2020. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020. PMID: 32284771 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and safety of the Impella ventricular assist device for high-risk percutaneous coronary interventions: A systematic review.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2018 Jun;91(7):1250-1260. doi: 10.1002/ccd.27316. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2018. PMID: 28941078
-
The cost-effectiveness of a new percutaneous ventricular assist device for high-risk PCI patients: mid-stage evaluation from the European perspective.J Med Econ. 2013;16(3):381-90. doi: 10.3111/13696998.2012.762004. Epub 2013 Jan 9. J Med Econ. 2013. PMID: 23301850
-
Clinical and economic effectiveness of percutaneous ventricular assist devices for high-risk patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.J Invasive Cardiol. 2015 Mar;27(3):148-54. J Invasive Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25740967 Review.
-
[Temporary percutaneous ventricular assist devices for cardiogenic shock and high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention: a systematic literature review].G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2020 Feb;21(2):128-137. doi: 10.1714/3300.32706. G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2020. PMID: 32051636 Italian.
Cited by
-
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Cardiac Indications in Adults: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020 Mar 6;20(8):1-121. eCollection 2020. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020. PMID: 32284771 Free PMC article.
-
Impella versus VA-ECMO for the treatment of patients with cardiogenic shock: the Impella Network Project - observational study protocol for cost-effectiveness and budget impact analyses.BMJ Open. 2024 Jun 26;14(6):e078358. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-078358. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38926145 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical circulatory support with Impella in percutaneous coronary intervention: current status.Am Heart J Plus. 2020 Nov 25;1:100002. doi: 10.1016/j.ahjo.2020.100002. eCollection 2021 Jan. Am Heart J Plus. 2020. PMID: 38560363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump During Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction With High Thrombus Burden and Cardiogenic Shock.Cureus. 2023 Jan 25;15(1):e34188. doi: 10.7759/cureus.34188. eCollection 2023 Jan. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36843698 Free PMC article.
-
Early cardiac unloading with ImpellaCP™ in acute myocardial infarction with ventricular septal defect.ESC Heart Fail. 2020 Apr;7(2):708-713. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12622. Epub 2020 Feb 11. ESC Heart Fail. 2020. PMID: 32043814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rihal CS, Naidu SS, Givertz MM, Szeto WY, Burke JA, Kapur NK, et al. 2015 SCAI/ACC/HFSA/STS clinical expert consensus statement on the use of percutaneous mechanical circulatory support devices in cardiovascular care (Endorsed by the American Heart Association, the Cardiological Society of India, and Sociedad Latino Americana de Cardiologia Intervencion; Affirmation of Value by the Canadian Association of Interventional Cardiology - Association Canadienne de Cardiologie d'intervention). J Card Fail. 2015;21(6):499–518. - PubMed
-
- Kar B, Basra SS, Shah NR, Loyalka P. Percutaneous circulatory support in cardiogenic shock: interventional bridge to recovery. Circulation. 2012;125(14):1809–17. - PubMed
-
- Babaev A, Frederick PD, Pasta DJ, Every N, Sichrovsky T, Hochman JS, et al. Trends in management and outcomes of patients with acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock. JAMA. 2005;294(4):448–54. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg RJ, Samad NA, Yarzebski J, Gurwitz J, Bigelow C, Gore JM. Temporal trends in cardiogenic shock complicating acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(15):1162–8. - PubMed
-
- Dixon SR, Henriques JP, Mauri L, Sjauw K, Civitello A, Kar B, et al. A prospective feasibility trial investigating the use of the Impella 2.5 system in patients undergoing high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention (the PROTECT I trial): initial U.S. experience. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2009;2(2):91–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
