Shared effects of the clusterin gene on the default mode network among individuals at risk for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 28233427
- PMCID: PMC6492680
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12682
Shared effects of the clusterin gene on the default mode network among individuals at risk for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Aims: To explore the common effects of the clusterin (CLU) rs11136000 variant on the default mode network (DMN) in amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) subjects and remitted geriatric depression (RGD) subjects.
Methods: Fifty-one aMCI subjects, 38 RGD subjects, and 64 cognitively normal elderly subjects underwent resting-state fMRI scans and neuropsychological tests at both baseline and a 35-month follow-up. Posterior cingulate cortex seed-based functional connectivity (FC) analysis was used to obtain the DMN patterns.
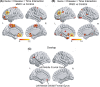
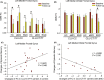
Results: A CLU gene×disease×time interaction for aMCI subjects was mainly detected in the core cortical midline structures of the DMN, and the interaction for RGD subjects was mainly detected in the limbic system. However, they overlapped in two frontal regions, where consistent effects of the CLU gene on FC alterations were found between aMCI and RGD groups. Furthermore, the alterations of FC with frontal, parietal, and limbic regions compensated for episodic memory impairments in CLU-CT/TT carriers, while no such compensation was found in CLU-CC carriers.
Conclusion: The CLU gene could consistently affect the DMN FC with frontal regions among individuals at risk for Alzheimer's disease, and the CLU-T allele was associated with more compensatory neural processes in DMN changes.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; clusterin; default mode network; geriatric depression; mild cognitive impairment.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunity factor contributes to altered brain functional networks in individuals at risk for Alzheimer's disease: Neuroimaging-genetic evidence.Brain Behav Immun. 2016 Aug;56:84-95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.02.015. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Brain Behav Immun. 2016. PMID: 26899953
-
Altered intrinsic default mode network functional connectivity in patients with remitted geriatric depression and amnestic mild cognitive impairment.Int Psychogeriatr. 2022 Aug;34(8):703-714. doi: 10.1017/S1041610221001174. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Int Psychogeriatr. 2022. PMID: 34635195
-
The apolipoprotein E gene affects the three-year trajectories of compensatory neural processes in the left-lateralized hippocampal network.Brain Imaging Behav. 2017 Oct;11(5):1446-1458. doi: 10.1007/s11682-016-9623-5. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017. PMID: 27734307
-
Functional brain connectivity using fMRI in aging and Alzheimer's disease.Neuropsychol Rev. 2014 Mar;24(1):49-62. doi: 10.1007/s11065-014-9249-6. Epub 2014 Feb 23. Neuropsychol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24562737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between clusterin concentration and dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Feb;34(1):129-140. doi: 10.1007/s11011-018-0325-0. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Metab Brain Dis. 2019. PMID: 30291488
Cited by
-
Disrupted functional and structural connectivity within default mode network contribute to WMH-related cognitive impairment.Neuroimage Clin. 2019;24:102088. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.102088. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Neuroimage Clin. 2019. PMID: 31795048 Free PMC article.
-
The compensatory phenomenon of the functional connectome related to pathological biomarkers in individuals with subjective cognitive decline.Transl Neurodegener. 2020 May 27;9(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40035-020-00201-6. Transl Neurodegener. 2020. PMID: 32460888 Free PMC article.
-
Association study of selenium-related gene polymorphisms with geriatric depression in China.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Apr 25;102(17):e33594. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033594. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37115082 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced White Matter Integrity With Cognitive Impairments in End Stage Renal Disease.Front Psychiatry. 2018 Apr 19;9:143. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00143. eCollection 2018. Front Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29725309 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation analysis on purified neurons and glia dissects age and Alzheimer's disease-specific changes in the human cortex.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018 Jul 25;11(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13072-018-0211-3. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018. PMID: 30045751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oda T, Wals P, Osterburg HH, et al. Clusterin (apoJ) alters the aggregation of amyloid beta‐peptide (A beta 1‐42) and forms slowly sedimenting A beta complexes that cause oxidative stress. Exp Neurol. 1995;136:22–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

