Antimicrobial activity of biogenically produced spherical Se-nanomaterials embedded in organic material against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus strains on hydroxyapatite-coated surfaces
- PMID: 28233476
- PMCID: PMC5481514
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.12700
Antimicrobial activity of biogenically produced spherical Se-nanomaterials embedded in organic material against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus strains on hydroxyapatite-coated surfaces
Abstract
In an effort to prevent the formation of pathogenic biofilms on hydroxyapatite (HA)-based clinical devices and surfaces, we present a study evaluating the antimicrobial efficacy of Spherical biogenic Se-Nanostructures Embedded in Organic material (Bio Se-NEMO-S) produced by Bacillus mycoides SelTE01 in comparison with two different chemical selenium nanoparticle (SeNP) classes. These nanomaterials have been studied as potential antimicrobials for eradication of established HA-grown biofilms, for preventing biofilm formation on HA-coated surfaces and for inhibition of planktonic cell growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa NCTC 12934 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923. Bio Se-NEMO resulted more efficacious than those chemically produced in all tested scenarios. Bio Se-NEMO produced by B. mycoides SelTE01 after 6 or 24 h of Na2 SeO3 exposure show the same effective antibiofilm activity towards both P. aeruginosa and S. aureus strains at 0.078 mg ml-1 (Bio Se-NEMO6 ) and 0.3125 mg ml-1 (Bio Se-NEMO24 ). Meanwhile, chemically synthesized SeNPs at the highest tested concentration (2.5 mg ml-1 ) have moderate antimicrobial activity. The confocal laser scanning micrographs demonstrate that the majority of the P. aeruginosa and S. aureus cells exposed to biogenic SeNPs within the biofilm are killed or eradicated. Bio Se-NEMO therefore displayed good antimicrobial activity towards HA-grown biofilms and planktonic cells, becoming possible candidates as new antimicrobials.
© 2017 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Applied Microbiology.
Figures
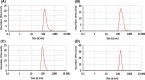



 Bio Se‐
Bio Se‐ Bio Se‐
Bio Se‐
 L‐cys Se
L‐cys Se Asc Se
Asc Se
 Bio Se‐
Bio Se‐ Bio Se‐
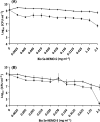
Bio Se‐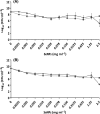
 L‐cys Se
L‐cys Se Asc Se
Asc Se
 Bio Se‐
Bio Se‐ Bio Se‐
Bio Se‐
 L‐cys Se
L‐cys Se Asc Se
Asc Se

References
-
- Ahmad, A. , Mukherjee, P. , Senapati, S. , Mandal, D. , Khan, M.S.I. , Kumar, R. , and Sastry, M. (2003) Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium oxysporum . Colloids Surf B 28: 313–318.
-
- Alhede, M. , Jensen, P. , Givskov, M. , and Bjarnshot, T. (2009) Biofilm medical importance. Biotechnology 12: e6581112.
-
- Ankamwar, B. , Chaudhary, M. , and Sastry, M. (2005) Gold nanoparticles biologically synthesized using Tamarind leaf extract and potential application in vapour sensing. Synth React Inorg, Met‐Org, Nano‐Met Chem 35: 19–26.
-
- Bhainsa, K.C. , and D'Souza, S.F. (2006) Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus . Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 47: 160–164. - PubMed
-
- Bigger, J.W. (1944) Treatment of Staphylococcal infections with penicillin by intermittent sterilization. Lancet 244: 497–500.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

