Identification and Characterization of Enzymes Catalyzing Pyrazolopyrimidine Formation in the Biosynthesis of Formycin A
- PMID: 28233490
- PMCID: PMC5467530
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00355
Identification and Characterization of Enzymes Catalyzing Pyrazolopyrimidine Formation in the Biosynthesis of Formycin A
Abstract
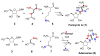
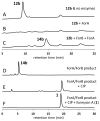
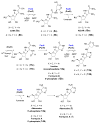
Genome scanning of Streptomyces kaniharaensis, the producer of formycin A, reveals two sets of purA, purB, purC, and purH genes. The Pur enzymes catalyze pyrimidine assembly of purine nucleobases. To test whether enzymes encoded by the second set of pur genes catalyze analogous transformations in formycin biosynthesis, formycin B 5'-phosphate was synthesized and shown to be converted by ForA and ForB to formycin A 5'-phosphate. These results support that For enzymes are responsible for formycin formation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of the Formycin A Biosynthetic Gene Cluster from Streptomyces kaniharaensis Illustrates the Interplay between Biological Pyrazolopyrimidine Formation and de Novo Purine Biosynthesis.J Am Chem Soc. 2019 Apr 17;141(15):6127-6131. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b00241. Epub 2019 Apr 8. J Am Chem Soc. 2019. PMID: 30942582 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the C-Glycoside Synthases during Biosynthesis of the Pyrazole-C-Nucleosides Formycin and Pyrazofurin.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Nov 11;58(46):16512-16516. doi: 10.1002/anie.201910356. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31518483 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of formycin. Formation of formycin from formycin B.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1975 Dec;28(12):965-73. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.28.965. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1975. PMID: 1206009
-
Holomycin, a dithiolopyrrolone compound produced by Streptomyces clavuligerus.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Feb;98(3):1023-30. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5410-z. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24323287 Review.
-
Nature's combinatorial biosynthesis and recently engineered production of nucleoside antibiotics in Streptomyces.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Apr;33(4):66. doi: 10.1007/s11274-017-2233-6. Epub 2017 Mar 4. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28260195 Review.
Cited by
-
PMP-diketopiperazine adducts form at the active site of a PLP dependent enzyme involved in formycin biosynthesis.Chem Commun (Camb). 2019 Nov 28;55(96):14502-14505. doi: 10.1039/c9cc06975e. Chem Commun (Camb). 2019. PMID: 31730149 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Investigation into Formycin A and Pyrazofurin A Biosynthesis Reveals Branch Pathways for the Construction of C-Nucleoside Scaffolds.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Jan 7;86(2):e01971-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01971-19. Print 2020 Jan 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31676476 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Formycin A Biosynthetic Gene Cluster from Streptomyces kaniharaensis Illustrates the Interplay between Biological Pyrazolopyrimidine Formation and de Novo Purine Biosynthesis.J Am Chem Soc. 2019 Apr 17;141(15):6127-6131. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b00241. Epub 2019 Apr 8. J Am Chem Soc. 2019. PMID: 30942582 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Sequence of Streptomyces kaniharaensis Shomura and Niida SF-557.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020 Apr 2;9(14):e01434-19. doi: 10.1128/MRA.01434-19. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020. PMID: 32241862 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of N-Heteroaryl C-Glycosides and Polyhydroxylated Alkanes with Diaryl Groups from Unprotected Sugars.ACS Omega. 2024 Nov 27;9(50):49618-49624. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c07671. eCollection 2024 Dec 17. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39713645 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

