A cardiac contouring atlas for radiotherapy
- PMID: 28233564
- PMCID: PMC5356506
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.01.008
A cardiac contouring atlas for radiotherapy
Abstract
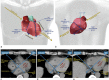
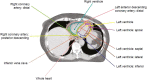
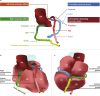
Background and purpose: The heart is a complex anatomical organ and contouring the cardiac substructures is challenging. This study presents a reproducible method for contouring left ventricular and coronary arterial segments on radiotherapy CT-planning scans.
Material and methods: Segments were defined from cardiology models and agreed by two cardiologists. Reference atlas contours were delineated and written guidelines prepared. Six radiation oncologists tested the atlas. Spatial variation was assessed using the DICE similarity coefficient (DSC) and the directed Hausdorff average distance (d→H,avg). The effect of spatial variation on doses was assessed using six different breast cancer regimens.
Results: The atlas enabled contouring of 15 cardiac segments. Inter-observer contour overlap (mean DSC) was 0.60-0.73 for five left ventricular segments and 0.10-0.53 for ten coronary arterial segments. Inter-observer contour separation (mean d→H,avg) was 1.5-2.2mm for left ventricular segments and 1.3-5.1mm for coronary artery segments. This spatial variation resulted in <1Gy dose variation for most regimens and segments, but 1.2-21.8Gy variation for segments close to a field edge.
Conclusions: This cardiac atlas enables reproducible contouring of segments of the left ventricle and main coronary arteries to facilitate future studies relating cardiac radiation doses to clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Atlas; Cardiac structures; Contouring; Radiotherapy CT-planning scans.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Darby S.C., Ewertz M., McGale P. Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:987–998. - PubMed
-
- Gagliardi G., Constine L.S., Moiseenko V. Radiation dose–volume effects in the heart. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;76:S77–S85. - PubMed
-
- Maraldo M.V., Brodin N.P., Vogelius I.R. Risk of developing cardiovascular disease after involved node radiotherapy versus mantle field for Hodgkin lymphoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83:1232–1237. - PubMed
-
- Moignier A., Broggio D., Derreumaux S. Coronary stenosis risk analysis following Hodgkin lymphoma radiotherapy: a study based on patient specific artery segments dose calculation. Radiother Oncol. 2015;117:467–472. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

