The single nucleotide variant rs12722489 determines differential estrogen receptor binding and enhancer properties of an IL2RA intronic region
- PMID: 28234966
- PMCID: PMC5325477
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172681
The single nucleotide variant rs12722489 determines differential estrogen receptor binding and enhancer properties of an IL2RA intronic region
Abstract
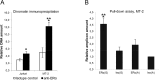
We studied functional effect of rs12722489 single nucleotide polymorphism located in the first intron of human IL2RA gene on transcriptional regulation. This polymorphism is associated with multiple autoimmune conditions (rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis). Analysis in silico suggested significant difference in the affinity of estrogen receptor (ER) binding site between alternative allelic variants, with stronger predicted affinity for the risk (G) allele. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay showed that purified human ERα bound only G variant of a 32-bp genomic sequence containing rs12722489. Chromatin immunoprecipitation demonstrated that endogenous human ERα interacted with rs12722489 genomic region in vivo and DNA pull-down assay confirmed differential allelic binding of amplified 189-bp genomic fragments containing rs12722489 with endogenous human ERα. In a luciferase reporter assay, a kilobase-long genomic segment containing G but not A allele of rs12722489 demonstrated enhancer properties in MT-2 cell line, an HTLV-1 transformed human cell line with a regulatory T cell phenotype.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multiple transcription factor elements collaborate with estrogen receptor alpha to activate an inducible estrogen response element in the NKG2E gene.Endocrinology. 2007 Jul;148(7):3449-58. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-1632. Epub 2007 Mar 29. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17395694
-
Multiple single nucleotide polymorphisms in the first intron of the IL2RA gene affect transcription factor binding and enhancer activity.Gene. 2017 Feb 20;602:50-56. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.11.032. Epub 2016 Nov 19. Gene. 2017. PMID: 27876533
-
Interleukin 2 receptor α gene polymorphism and risk of multiple sclerosis: a meta-analysis.J Int Med Res. 2011;39(5):1625-35. doi: 10.1177/147323001103900505. J Int Med Res. 2011. PMID: 22117963
-
A genetic link between CXCR5 and IL2RA gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to multiple sclerosis.Neurol Res. 2018 Dec;40(12):1040-1047. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2018.1517110. Neurol Res. 2018. PMID: 30352019
-
A distal estrogen responsive element upstream the cap site of human transthyretin gene is an enhancer-like element upon ERα and/or ERβ transactivation.Gene. 2013 Sep 25;527(2):469-76. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.06.078. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23860318
Cited by
-
Analysis of herpesvirus infection and genome single nucleotide polymorphism risk factors in multiple sclerosis, Volga federal district, Russia.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 14;13:1010605. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1010605. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36451826 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in HLA-DRA, IL2RA , and HMGB1 Genes in Multiple Sclerosis.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 Jul;9(2):198-208. doi: 10.29252/rbmb.9.2.199. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 33178870 Free PMC article.
-
The GALNT14 Genotype Predicts Postoperative Outcome of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.J Clin Med. 2019 Dec 16;8(12):2225. doi: 10.3390/jcm8122225. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31888240 Free PMC article.
-
The landscape of GWAS validation; systematic review identifying 309 validated non-coding variants across 130 human diseases.BMC Med Genomics. 2022 Apr 1;15(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01216-w. BMC Med Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35365203 Free PMC article.
-
Severe chronic kidney disease environment reduced calcium-sensing receptor expression in parathyroid glands of adenine-induced rats even without high phosphorus diet.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Jun 9;21(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-01880-z. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32517664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hindorff LA, Sethupathy P, Junkins HA, Ramos EM, Mehta JP, Collins FS, et al. Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106(23):9362–7. 10.1073/pnas.0903103106 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fehrmann RS, Jansen RC, Veldink JH, Westra HJ, Arends D, Bonder MJ, et al. Trans-eQTLs reveal that independent genetic variants associated with a complex phenotype converge on intermediate genes, with a major role for the HLA. PLoS genetics. 2011;7(8):e1002197 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002197 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brian Jo YH, Strober Benjamin J., Parsana Princy, Aguet François, Brown Andrew A., Castel Stephane, Gamazon Eric R., Gewirtz Ariel, Gliner Genna, Han Buhm, He Amy Z., Yong Kang Eun, McDowell Ian C., Li Xiao, Mohammadi Pejman, Peterson Christine B., Quon Gerald, Saha Ashis, Segrè Ayellet V., Hoon Sul Jae, Sullivan Timothy J., Ardlie Kristin G., Brown Christopher D., Conrad Donald F., Cox Nancy J., Dermitzakis Emmanouil T., Eskin Eleazar, Kellis Manolis, Lappalainen Tuuli, Sabatti Chiara, GTEx Consortium, Engelhardt Barbara E., Battle Alexis. Distant regulatory effects of genetic variation in multiple human tissues. 2016. 10.1101/074419. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

