The herbal formula KH-204 is protective against erectile dysfunction by minimizing oxidative stress and improving lipid profiles in a rat model of erectile dysfunction induced by hypercholesterolaemia
- PMID: 28235412
- PMCID: PMC5324223
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1588-4
The herbal formula KH-204 is protective against erectile dysfunction by minimizing oxidative stress and improving lipid profiles in a rat model of erectile dysfunction induced by hypercholesterolaemia
Abstract
Background: Hypercholesterolaemia (HC) is a major risk factor for ischemic heart disease and is also known to be a risk factor for erectile dysfunction (ED). ED caused by HC is thought to be related to HC-induced oxidative stress damage in the vascular endothelium and erectile tissue. KH-204 is an herbal formula with a strong antioxidant effect. We evaluated the effects of KH-204 on erectile function in a rat model of HC-induced ED.
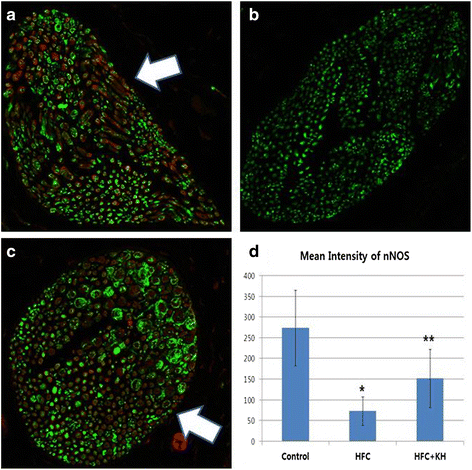
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (6 weeks old) were divided into normal control, high-fat and cholesterol diet (HFC), and HFC with KH-204 treatment (HFC + KH) groups (n = 12 each). Normal control group rats were fed normal chow diet. HFC and HFC + KH group rats were fed high-fat and cholesterol diets and treated with or without daily oral doses of KH-204 for 12 weeks. Subsequently, intracavernous pressure (ICP) and mean arterial pressure (MAP) were measured, and lipid profiles, expression of endothelial (eNOS) and neuronal (nNOS) nitric oxide synthase, oxidative stress (8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine), and ratio of smooth muscle cells and collagen fibres were evaluated in the serum and corpora tissue.
Results: Compared to the HFC group, the HFC + KH group showed statistically significant increases in peak ICP and ICP/MAP ratio, expression of eNOS and nNOS, and ratio of smooth muscle cells and collagen fibres (p < 0.05). The HFC + KH group also showed statistically significant decreases in oxidative stress (p < 0.05). Further the lipid profiles of this group were ameliorated compared to those of the HFC group (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: The current study shows that the antioxidant and hypolipidemic effects of KH-204 are effective in ameliorating ED by restoring endothelial dysfunction and suggests that KH-204 may be a potential therapeutic agent for ED by correcting the fundamental cause of ED.
Keywords: Erectile dysfunction; Hypercholesterolaemia; Oxidative stress.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cyanidin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside concentrated materials from mulberry fruit have a potency to protect erectile function by minimizing oxidative stress in a rat model of diabetic erectile dysfunction.Urol Int. 2012;88(4):470-6. doi: 10.1159/000336136. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Urol Int. 2012. PMID: 22433441
-
Effect of a Chinese herbal medicine mixture on a rat model of hypercholesterolemic erectile dysfunction.J Urol. 2000 Nov;164(5):1798-801. J Urol. 2000. PMID: 11025772
-
An oral formulation of angiotensin-(1-7) reverses corpus cavernosum damages induced by hypercholesterolemia.J Sex Med. 2013 Oct;10(10):2430-42. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12262. Epub 2013 Jul 24. J Sex Med. 2013. PMID: 23890028
-
Melatonin prevents deterioration of erectile function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats via sirtuin-1 expression.Andrologia. 2020 Oct;52(9):e13639. doi: 10.1111/and.13639. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Andrologia. 2020. PMID: 32478903 Review.
-
Posttranslational modification of constitutive nitric oxide synthase in the penis.J Androl. 2009 Jul-Aug;30(4):352-62. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.108.006999. Epub 2009 Apr 2. J Androl. 2009. PMID: 19342700 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic effects of extracorporeal shockwave therapy and modified Ojayeonjonghwan on erectile dysfunction in an animal model of diabetes.Investig Clin Urol. 2019 Jul;60(4):285-294. doi: 10.4111/icu.2019.60.4.285. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Investig Clin Urol. 2019. PMID: 31294138 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Antifibrotic Effect of a Herbal Formulation In Vitro and in the Experimental Andropause via Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:6024839. doi: 10.1155/2017/6024839. Epub 2017 Sep 17. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 29075365 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a combination of herbal extracts (modified Ojayeonjonghwan (Wuzi Yanzong wan)) on partial urethral obstruction-induced detrusor overactivity in rats: impact on the nitric oxide pathway and oxidative stress.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Mar 14;19(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2467-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 30871532 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Calorie Restriction and Exercise on Age-Related Alterations in Corpus Cavernosum.Front Physiol. 2020 Feb 18;11:45. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00045. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32132927 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy in an obesity-associated erectile dysfunction rat model.BJU Int. 2018 Jul;122(1):133-142. doi: 10.1111/bju.14202. Epub 2018 Apr 17. BJU Int. 2018. PMID: 29573106 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

