Inducible microRNA-214 contributes to the suppression of NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response via targeting myd88 gene in fish
- PMID: 28235799
- PMCID: PMC5392675
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.777078
Inducible microRNA-214 contributes to the suppression of NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response via targeting myd88 gene in fish
Abstract
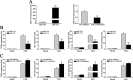
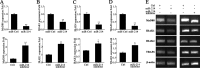
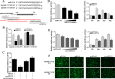
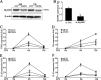
Upon recognition of bacterial pathogens by pattern recognition receptors, cells are activated to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines and type I IFN by multiple signaling pathways. Every step of the process must be precisely regulated to prevent dysregulation. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been shown to be important regulators with profound effects on inflammatory response. Nevertheless, the miRNA-mediated regulatory mechanism remains unclear in fish species. Here, we addressed the role of miiuy croaker miR-214 in the bacteria triggered inflammatory response. miR-214 could significantly be up-regulated by Vibro harveyi and LPS stimulation. Up-regulating miR-214 subsequently inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines by targeting myd88 to avoid excessive inflammation. Moreover, the negative regulatory mechanism of miR-214 has been demonstrated to be via the myd88-mediated NF-κB pathway. This is the first to focus on miR-214 acting as the negative regulator involved in the bacteria-triggered inflammatory response and thus may provide knowledge on the host-cell regulator responses to microbial infection.
Keywords: MyD88; NF-κB; cellular immune response; excessive inflammation; gene regulation; microRNA (miRNA); microRNA mechanism; microRNA-214; myeloid differentiation primary response gene (88) (MYD88); negatively regulation.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures



References
-
- Takeuchi O., and Akira S. (2010) Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 140, 805–820 - PubMed
-
- Kawai T., and Akira S. (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 11, 373–384 - PubMed
-
- Kawai T., and Akira S. (2011) Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity 34, 637–650 - PubMed
-
- Takeda K., Kaisho T., and Akira S. (2003) Toll-like receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21, 335–376 - PubMed
-
- Lang C. H., Silvis C., Deshpande N., Nystrom G., and Frost R. A. (2003) Endotoxin stimulates in vivo expression of inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin-1β, -6, and high-mobility-group protein-1 in skeletal muscle. Shock 19, 538–546 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

