CRL2Lrr1 promotes unloading of the vertebrate replisome from chromatin during replication termination
- PMID: 28235849
- PMCID: PMC5358724
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.291799.116
CRL2Lrr1 promotes unloading of the vertebrate replisome from chromatin during replication termination
Abstract
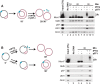
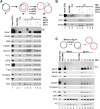
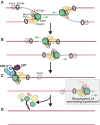
A key event during eukaryotic replication termination is the removal of the CMG helicase from chromatin. CMG unloading involves ubiquitylation of its Mcm7 subunit and the action of the p97 ATPase. Using a proteomic screen in Xenopus egg extracts, we identified factors that are enriched on chromatin when CMG unloading is blocked. This approach identified the E3 ubiquitin ligase CRL2Lrr1, a specific p97 complex, other potential regulators of termination, and many replisome components. We show that Mcm7 ubiquitylation and CRL2Lrr1 binding to chromatin are temporally linked and occur only during replication termination. In the absence of CRL2Lrr1, Mcm7 is not ubiquitylated, CMG unloading is inhibited, and a large subcomplex of the vertebrate replisome that includes DNA Pol ε is retained on DNA. Our data identify CRL2Lrr1 as a master regulator of replisome disassembly during vertebrate DNA replication termination.
Keywords: CMG; DNA replication; p97; replication termination; ubiquitin.
© 2017 Dewar et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures



Comment in
-
Conducting the finale of DNA replication.Genes Dev. 2017 Feb 1;31(3):226-227. doi: 10.1101/gad.297184.117. Genes Dev. 2017. PMID: 28270514 Free PMC article.
-
Two paths to let the replisome go.Cell Death Differ. 2017 Jul;24(7):1140-1141. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.75. Epub 2017 May 19. Cell Death Differ. 2017. PMID: 28524853 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Buchberger A, Schindelin H, Hanzelmann P. 2015. Control of p97 function by cofactor binding. FEBS Lett 589: 2578–2589. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
