Influence of Membrane Receptor Lateral Diffusion on the Short-Term Depression of Acetylcholine-Induced Current in Helix Neurons
- PMID: 28236056
- PMCID: PMC11482138
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-017-0475-3
Influence of Membrane Receptor Lateral Diffusion on the Short-Term Depression of Acetylcholine-Induced Current in Helix Neurons
Abstract
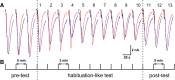
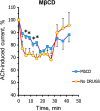
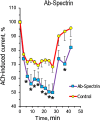
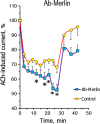
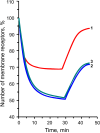
We have studied how various drugs increasing the rate of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) lateral diffusion affect the depression of ACh-induced current in land snail Helix lucorum neurons responsible for defensive behavior. The acetylcholine (ACh) iontophoretic application protocol imitated the behavioral habituation protocol for the intact animal. We found that the drugs decreasing cholesterol level in cell membranes as methyl-β-cyclodextrin 1 mM and Ro 48-8071 2 µM, and polyclonal antibodies to actin-binding proteins as spectrin 5 µg/ml and merlin 2.5 µg/ml have changed the dynamic of ACh-current depression. The nAChRs lateral diffusion coefficient was obtained by fluorescence recovery after photobleaching. A curve fitting model specially created for analysis of short-term choline sensitivity depression in snail neurons helped us evaluate separately the contribution of nAChRs lateral diffusion, their endocytosis and exocytosis to observed effects during electrophysiological experiments. Taken together, we hypothesize that nAChRs lateral diffusion plays an important role in the cellular correlate of habituation in land snail Helix lucorum neurons.
Keywords: Acetylcholine receptors; Acetylcholine-induced current, Habituation-like short-term depression; Command Helix neurons; Lateral diffusion; Methyl-β-cyclodextrin; Ro 48-8071; Spectrin, merlin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mobility of acetylcholine receptors in command Helix lucorum neurons in a cellular analog of habituation.Invert Neurosci. 2013 Dec;13(2):135-50. doi: 10.1007/s10158-013-0155-z. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Invert Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23591591
-
Habituation-Like Decrease of Acetylcholine-Induced Inward Current in Helix Command Neurons: Role of Microtubule Motor Proteins.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Jul;35(5):703-12. doi: 10.1007/s10571-015-0165-y. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25687906 Free PMC article.
-
[The Na,K pump regulates a decrease in the cholinosensitivity of the neurons in the snail Helix lucorum taurica Kryn in a cellular analog of habituation: its dependence on intracellular calcium].Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2000 Sep-Oct;50(5):855-66. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2000. PMID: 11085001 Russian.
-
[The role of serine/threonine and tyrosine protein kinases in the depression of cholinosensitivity in Helix lucorum neurons in the cellular correlate of habituation].Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2011 Jul-Aug;61(4):459-75. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2011. PMID: 21961321 Russian.
-
Cholinergic receptor exocytosis under conditions of depression of acetylcholine-induced current in edible snail neurons in cellular analogue of habituation.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2012 Aug;153(4):424-7. doi: 10.1007/s10517-012-1731-7. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22977835 English, Russian.
References
-
- Apodaca G (2001) Endocytic traffic in polarized epithelial cells: role of the actin and microtubule cytoskeleton. Traffic 2:149–159 - PubMed
-
- Baenziger JE, Morris ML, Darsaut TE, Ryan SE (2000) Effect of membrane lipid composition on the conformational equilibria of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem 275:777–784 - PubMed
-
- Baines AJ (2010) The spectrin-ankyrin-4.1-adducin membrane skeleton: adapting eukaryotic cells to the demands of animal life. Protoplasma 244:99–131. doi:10.1007/s00709-010-0181-1 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

