Antazoline-insights into drug-induced electrocardiographic and hemodynamic effects: Results of the ELEPHANT II substudy
- PMID: 28236352
- PMCID: PMC6931461
- DOI: 10.1111/anec.12441
Antazoline-insights into drug-induced electrocardiographic and hemodynamic effects: Results of the ELEPHANT II substudy
Abstract
Background: Antazoline is an old antihistaminic and new antiarrhythmic agent with unknown mechanisms of action which recently has been shown to effectively terminate atrial fibrillation. The aim of study was to examine the effects of antazoline on hemodynamic and ECG parameters.
Methods: Antazoline was given intravenously in three 100 mg boluses to 10 healthy volunteers (four males, mean age 40 + 11 years). Hemodynamic and ECG parameters were measured using impedance cardiography [systolic (sBP), diastolic (dBP), mean (mBP) blood pressure, stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), total peripheral resistance (TPR) and heart rate (HR), P wave, PR interval, QRS complex, QT and corrected QT (QTcF) interval]. Plasma concentration of antazoline was also measured.
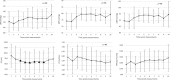
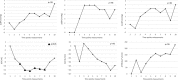
Results: Antazoline caused significant prolongation of P wave, QRS as well as QT and QTcF (101 ± 10 vs 110 ± 16 ms, p < .05, and 101 ± 12 vs 107 ± 12 ms, p < .05, 399 ± 27 vs 444 ± 23 ms, p < .05, and 403 ± 21 vs 448 ± 27 ms, p < .05, respectively). Also, a significant decrease in SV was noted (94.9 ± 21.8 vs 82.4 ± 19.6 ml, p < .05). A significant correlation between changes in plasma drug concentration and changes in CO, HR, and dBP was found.
Conclusions: Antazoline impairs slightly hemodynamics, significantly reducing SV. Significant prolongation of P wave and QRS duration corresponds to drug-induced prolongation of conduction, whereas QT prolongation represents drug-induced prolongation of repolarization.
Keywords: antazoline; antazoline concentration; antiarrhythmic agent; atrial fibrillation; hemodynamic and electrocardiographic effects.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Badyra, B. , Lisowski, B. , Borusewicz, M. , Piotrowski, R. , Kułakowski, P. , Wiśniowska, B. , & Polak, S . (2016). Interactions of antazoline with human ether‐à‐go‐go‐related gene channels. Kardiologia polska (Abstract Supplement), 74, 374–375.
-
- Balsam, P. , Koźluk, E. , Peller, M. , Piątkowska, A. , Lodziński, P. , Kiliszek, M. , … Opolski, G . (2015). Antazoline for termination of atrial fibrillation during the procedure of pulmonary veins isolation. Advances in Medical Sciences, 60, 231–235. - PubMed
-
- Camm, A. J. , Kirchhof, P. , Lip, G. Y. , Schotten, U. , Savelieva, I. , Ernst, S. , … Rutten, F. H . (2010). Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: The Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal, 31, 2369–2429. - PubMed
-
- Camm, A. J. , Lip, G. Y. , De Caterina, R. , Savelieva, I. , Atar, D. , Hohnloser, S. H. , … Kirchhof, P . (2012). 2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: An update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. European Heart Journal, 33(21), 2719–2747. - PubMed
-
- Cybulski, G. , Koźluk, E. , Michalak, E. , Niewiadomski, W. , & Piątkowska, A . (2004). Holter‐type impedance cardiography device. A system for continuous and non‐invasive monitoring of cardiac haemodynamics. Kardiologia polska, 61, 138–146. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

