Development a rapid and accurate multiplex real time PCR method for the detection Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma hominis
- PMID: 28238212
- PMCID: PMC6817121
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22126
Development a rapid and accurate multiplex real time PCR method for the detection Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma hominis
Abstract
Background: Sexually transmitted diseases easily spread among sexually active people and often have no symptoms. Rapid and accurate method for detecting these infections are necessary in early stages. The traditional detection methods of them are difficult and time-consuming.
Methods: In this study, multiplex real time PCR was optimized for rapid identification of Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma hominis in a single tube and was performed with our designed primers. The sensitivity test was carried out to designed primers with diluted genomic DNA. To defined the specificity, non STD bacteria were used as DNA template.
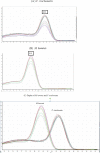
Results: This study indicated that the developed multiplex real time PCR can be an effective alternative procedure to the conventional methods for rapid and accurate identification of C Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma hominis. Multiplex real-time PCR Results of them were checked with melting curves. The sensitivity of our designed primer by multiplex real time PCR for Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma hominis were 4.78×1010 and 8.35×1010 , respectively, Which the primers did not amplify any product from a non-STD species.
Conclusions: Multiplex real time PCR by our new primers and analysis of melting curves were successfully usable for rapid and accurate detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma hominis. This assay instead of traditional culture method, has considerable potential to be rapid, accurate and highly sensitive molecular diagnostic tool for simultaneous and direct detection.
Keywords: Chlamydia trachomatis; Mycoplasma hominis; multiplex real time PCR.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Jahan F, Shamsuzzaman SM, Akter S. Diagnosis of common bacterial causes of urethritis in men by Gram stain, culture and multiplex PCR. Malays J Pathol. 2014;36:175–180. - PubMed
-
- Nisyrios G. Should the Australian defence force screen for genital Chlamydia trachomatis infection? Aust Defence Force Health. 2006;7:1–20.
-
- Wallesar S, Salkeld G, Donovan B. The cost effectiveness of screening forgenital Chlamydia trachomatis infection in Australia. Sex Health. 2006;3:225–234. - PubMed
-
- Gdoura R, Kchaou W, Ammar KL, et al. Assessment of Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Ureaplasma parvum, Mycoplasma hominis and Mycoplasma genitalium in semen and first void urinespecimens of asymptomatic male partners of infertilecouples. J Androl. 2008;29:198–206. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials