Mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced Sertoli cell injury stimulates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in Fischer 344 rats
- PMID: 28238932
- PMCID: PMC5406244
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2017.02.013
Mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced Sertoli cell injury stimulates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in Fischer 344 rats
Abstract
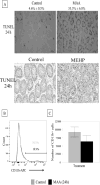
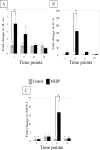
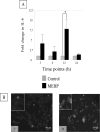
Exposure of rodents to the Sertoli cell (SC) toxicant mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (MEHP) has been reported to trigger an infiltration of macrophages into the testis in an age- and species-dependent manner. Here we challenge the hypothesis that the peripubertal rat-specific infiltration of macrophages after MEHP exposure is due, in part, to an increase in SC-specific inflammatory cytokine expression. To rule out that germ cell(GC) apoptosis itself is responsible for macrophage recruitment, rats were exposed to a direct GC toxicant, methoxyacetic acid (MAA), but no infiltration of macrophages was observed. Next, mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines were evaluated after MEHP exposure. IL-1α, IL-6, and MCP-1 expression were increased in vivo and correlated with macrophage infiltration in a species-specific manner. Additionally, IL-6 and MCP-1 expression was increased in SC-GC co-cultures and ASC-17D SCs. These results indicate that MEHP-injury in pubertal rats specifically stimulates secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and alters the immune microenvironment.
Keywords: Cytokines; Mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate; Sertoli cells; Testicular macrophages.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- O’Bryan MK, Hedger MP. Inflammatory networks in the control of spermatogenesis : chronic inflammation in an immunologically privileged tissue? Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;636:92–114. - PubMed
-
- Hedger MP, Winnall WR. Regulation of activin and inhibin in the adult testis and the evidence for functional roles in spermatogenesis and immunoregulation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012 Aug 15;359(1–2):30–42. - PubMed
-
- Campese AF, Grazioli P, de Cesaris P, Riccioli A, Bellavia D, Pelullo M, et al. Mouse Sertoli cells sustain de novo generation of regulatory T cells by triggering the notch pathway through soluble JAGGED1. Biol Reprod. 2014 Mar;90(3):53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

