Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy in a patient with Crohn's disease
- PMID: 28239323
- PMCID: PMC5323302
- DOI: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.1.124
Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy in a patient with Crohn's disease
Abstract
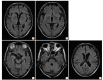
Metronidazole is a widely used antibiotic for the treatment of anaerobic bacterial infections. Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy (MIEP) is a rare but potentially reversible disease. The mechanism of MIEP remains unclear, and differences in the neurotoxic effects of oral versus intravenous (IV) metronidazole administration have not yet been determined. We report the case of a Crohn's disease (CD) patient who experienced encephalopathy immediately after a single IV dose of metronidazole following long-term exposure to the oral form of the drug. The 64-year-old man with intractable CD experienced a sudden change in mental status, aphasia, and muscle weakness after IV administration of metronidazole. He had previously taken metronidazole orally for 13 years and received intermittent IV metronidazole treatments for CD exacerbation. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed high-intensity signals in the bilateral medial thalamus and the midbrain and pontine tegmentum on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images. After discontinuation of metronidazole, the high-intensity brain MRI signals resolved and the patient's mental status dramatically improved; however, the patient exhibited mild cognitive dysfunction 2 months after the onset of encephalopathy.
Keywords: Crohn disease; Drug side effects; Metabolic encephalopathy; Metronidazole.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy in a patient with infectious colitis: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2011 Feb 14;5:63. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-5-63. J Med Case Rep. 2011. PMID: 21320332 Free PMC article.
-
Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy and inferior olivary hypertrophy: lesion analysis with diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient maps.Arch Neurol. 2003 Dec;60(12):1796-800. doi: 10.1001/archneur.60.12.1796. Arch Neurol. 2003. PMID: 14676060
-
Atypical metronidazole-induced encephalopathy in anaerobic brain abscess.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012 Sep;52(3):273-6. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2012.52.3.273. Epub 2012 Sep 30. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012. PMID: 23115678 Free PMC article.
-
Metronidazole-induced Encephalopathy: Case Report and Review Literature.Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2012 Jun;21(2):74-8. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2012. PMID: 22879116 Review.
-
[Clinical Characteristics of Metronidazole-induced Encephalopathy: A Report of Two Cases and a Review of 32 Japanese Cases in the Literature].Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2015 Sep;89(5):559-66. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi.89.559. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 26630786 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy: a systematic review.J Neurol. 2020 Jan;267(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s00415-018-9147-6. Epub 2018 Dec 7. J Neurol. 2020. PMID: 30536109
-
Reversible metronidazole-induced neurotoxicity after 10 weeks of therapy.BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Apr 20;2018:bcr2017223463. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-223463. BMJ Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29678819 Free PMC article.
-
MRI Findings and Topographic Distribution of Lesions in Metronidazole-Induced Encephalopathy.Cureus. 2022 Sep 14;14(9):e29145. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29145. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36282977 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency and Risk Factor Analysis for Metronidazole-Associated Neurologic Adverse Events.J Gen Intern Med. 2024 May;39(6):912-920. doi: 10.1007/s11606-023-08566-w. Epub 2023 Dec 13. J Gen Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 38093026 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic-induced neuropsychiatric toxicity: epidemiology, mechanisms and management strategies - a narrative literature review.Drugs Context. 2024 Jul 24;13:2024-3-3. doi: 10.7573/dic.2024-3-3. eCollection 2024. Drugs Context. 2024. PMID: 39072301 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Löfmark S, Edlund C, Nord CE. Metronidazole is still the drug of choice for treatment of anaerobic infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(Suppl 1):S16–S23. - PubMed
-
- Lamp KC, Freeman CD, Klutman NE, Lacy MK. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the nitroimidazole antimicrobials. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1999;36:353–373. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

