Celastrol Attenuates Multiple Sclerosis and Optic Neuritis in an Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Model
- PMID: 28239352
- PMCID: PMC5301323
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00044
Celastrol Attenuates Multiple Sclerosis and Optic Neuritis in an Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Model
Abstract
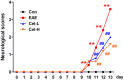
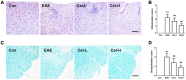
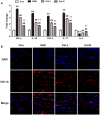
This study was aimed to evaluate the effects of celastrol, a natural compound with multiple bioactivities, on multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis (ON) in rat experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). EAE was induced in Sprague Dawley rats using myelin basic protein, and the animals received daily intraperitoneal injections of celastrol or vehicle for 13 days. The EAE rats showed abnormal neurobehavior and inflammatory infiltration and demyelination in the spinal cord. Significantly upregulated mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines interferon-γ and interleukin-17 and downregulated anti-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-4 were found in the spinal cord of EAE rats. In the study of ON, severely inflammatory responses like in the spinal cord were also seen in the optic nerve, as well as obvious microgliosis. Furthermore, activation of nuclear factor kappa-B and upregulated inducible nitric oxide synthase was observed in the optic nerve. In addition, apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells and dysregulation of apoptotic-associated proteins in the optic nerve were found in EAE rats. Treatment of celastrol potently restored these changes. In most of the indexes, the effects of high dose of celastrol were better than the low dose. Our data conclude that administration of celastrol attenuates multiple sclerosis and ON in EAE via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects. These findings provide new pre-clinical evidence for the use of celastrol in treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Keywords: apoptosis; celastrol; inflammation; multiple sclerosis; optic neuritis.
Figures



References
-
- Astry B., Venkatesha S. H., Laurence A., Christensen-Quick A., Garzino-Demo A., Frieman M. B., et al. (2015). Celastrol, a Chinese herbal compound, controls autoimmune inflammation by altering the balance of pathogenic and regulatory T cells in the target organ. Clin. Immunol. 157 228–238. 10.1016/j.clim.2015.01.011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benveniste E. N., Liu Y., McFarland B. C., Qin H. (2014). Involvement of the janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway in multiple sclerosis and the animal model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 34 577–588. 10.1089/jir.2014.0012 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

