Identification by Genome Mining of a Type I Polyketide Gene Cluster from Streptomyces argillaceus Involved in the Biosynthesis of Pyridine and Piperidine Alkaloids Argimycins P
- PMID: 28239372
- PMCID: PMC5300972
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00194
Identification by Genome Mining of a Type I Polyketide Gene Cluster from Streptomyces argillaceus Involved in the Biosynthesis of Pyridine and Piperidine Alkaloids Argimycins P
Abstract
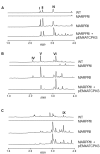
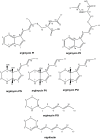
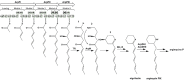
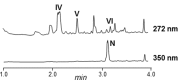
Genome mining of the mithramycin producer Streptomyces argillaceus ATCC 12956 revealed 31 gene clusters for the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, and allowed to predict the encoded products for 11 of these clusters. Cluster 18 (renamed cluster arp) corresponded to a type I polyketide gene cluster related to the previously described coelimycin P1 and streptazone gene clusters. The arp cluster consists of fourteen genes, including genes coding for putative regulatory proteins (a SARP-like transcriptional activator and a TetR-like transcriptional repressor), genes coding for structural proteins (three PKSs, one aminotransferase, two dehydrogenases, two cyclases, one imine reductase, a type II thioesterase, and a flavin reductase), and one gene coding for a hypothetical protein. Identification of encoded compounds by this cluster was achieved by combining several strategies: (i) inactivation of the type I PKS gene arpPIII; (ii) inactivation of the putative TetR-transcriptional repressor arpRII; (iii) cultivation of strains in different production media; and (iv) using engineered strains with higher intracellular concentration of malonyl-CoA. This has allowed identifying six new alkaloid compounds named argimycins P, which were purified and structurally characterized by mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Some argimycins P showed a piperidine ring with a polyene side chain (argimycin PIX); others contain also a fused five-membered ring (argimycins PIV-PVI). Argimycins PI-PII showed a pyridine ring instead, and an additional N-acetylcysteinyl moiety. These compounds seem to play a negative role in growth and colony differentiation in S. argillaceus, and some of them show weak antibiotic activity. A pathway for the biosynthesis of argimycins P is proposed, based on the analysis of proposed enzyme functions and on the structure of compounds encoded by the arp cluster.
Keywords: Streptomyces; alkaloid; cryptic; growth; piperidine; pyridine; thioester reductase; type I polyketide synthase.
Figures



References
-
- Aguirrezabalaga I., Olano C., Allende N., Rodriguez L., Braña A. F., Méndez C., et al. (2000). Identification and expression of genes involved in biosynthesis of L-oleandrose and its intermediate L-olivose in the oleandomycin producer Streptomyces antibioticus. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 44 1266–1275. 10.1128/AAC.44.5.1266-1275.2000 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aleku G. A., Man H., France S. P., Leipold F., Hussain S., Toca-Gonzalez L., et al. (2016). Stereoselectivity and structural characterization of an imine reductase (IRED) from Amycolatopsis orientalis. ACS Catal. 6 3880–3889. 10.1021/acscatal.6b00782 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

