A review on polymeric hydrogel membranes for wound dressing applications: PVA-based hydrogel dressings
- PMID: 28239493
- PMCID: PMC5315442
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2017.01.005
A review on polymeric hydrogel membranes for wound dressing applications: PVA-based hydrogel dressings
Abstract
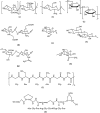
This review presents the past and current efforts with a brief description on the featured properties of hydrogel membranes fabricated from biopolymers and synthetic ones for wound dressing applications. Many endeavors have been exerted during past ten years for developing new artificial polymeric membranes, which fulfill the demanded conditions for the treatment of skin wounds. This review mainly focuses on representing specifications of ideal polymeric wound dressing membranes, such as crosslinked hydrogels compatible with wound dressing purposes. But as the hydrogels with single component have low mechanical strength, recent trends have offered composite or hybrid hydrogel membranes to achieve the typical wound dressing requirements.
Keywords: Biomedical applications; Hydrogels; Membranes; Skin substituent; Wound dressings.
Figures
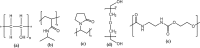

References
-
- Gibs I., Janik H. Review: synthetic polymer hydrogels for biomedical applications. Chem Chem Tech. 2010;4(4):297–304.
-
- Lim F., Sun A.M. Microencapsulated islets as bioartificial endocrine pancreas. Science. 1980;210:908–910. - PubMed
-
- Yannas, Gordon PL, Huang C, Silver FH, Burke, JF. Crosslinked Collagen-Mucopolysaccharide Composite Materials. U.S. Pat. 4,280,954 1981.
-
- Winter G.D. Formation of the scab and the rate of epithelization of superficial wounds in the skin of the young domestic pig. Nature. 1962;193:293–294. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

