Macrovascular and microvascular cerebral blood flow in adults at risk for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 28239641
- PMCID: PMC5318539
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dadm.2017.01.002
Macrovascular and microvascular cerebral blood flow in adults at risk for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: Capillary hypoperfusion is reported in asymptomatic adults at-risk for Alzheimer's disease (AD), but the extent that can be explained by reduced flow in intracranial arteries is unknown.
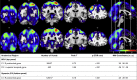
Methods: One hundred fifty-five asymptomatic adults enriched for AD risk (mean age 61 years) completed arterial spin labeling (pcASL) and 4D-flow MRI sequences. Voxel-wise regression models investigated the relationship between mean flow in bilateral cerebral arteries and capillary perfusion, and tested potential moderators of this relationship.
Results: Mean arterial blood flow through middle cerebral arteries (MCAs) and internal carotid arteries was positively associated with perfusion in large cortical clusters (P < .05, false discovery rate corrected). Trends were observed for the interactions MCA flow × age and MCA flow × cardiovascular risk on cerebral perfusion (P < .001, uncorrected).
Discussion: These findings provide evidence that capillary perfusion measured via pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling is strongly dependent on inflow from larger cerebral arteries. Further studies are warranted to investigate possible alterations between macrovascular and microvascular flow in advanced age and elevated cardiovascular risk in asymptomatic adults at risk for AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Arterial spin labeling; Cerebral blood flow; Cerebrovascular disease; Phase-contrast MRI; Vascular imaging.
Figures


References
-
- Shaw T.G., Mortel K.F., Meyer J.S., Rogers R.L., Hardenberg J., Cutaia M.M. Cerebral blood flow changes in benign aging and cerebrovascular disease. Neurology. 1984;34:855–862. - PubMed
-
- Kim S.M., Kim M.J., Rhee H.Y., Ryu C.W., Kim E.J., Petersen E.T. Regional cerebral perfusion in patients with Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: effect of APOE epsilon4 allele. Neuroradiology. 2013;55:25–34. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
