HLA-DQ β 1 alleles associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infectivity and EBV gp42 binding to cells
- PMID: 28239644
- PMCID: PMC5313076
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.85687
HLA-DQ β 1 alleles associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infectivity and EBV gp42 binding to cells
Abstract
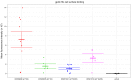
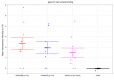
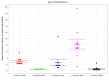
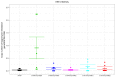
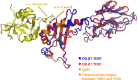
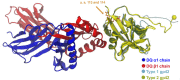
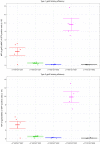
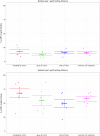
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infects B cells and ~95% of adults are infected. EBV glycoprotein gp42 is essential for entry of virus into B cells. EBV gp42 binds to the β1 chain of HLA-DQ, -DR, and -DP on B cells, and uses these molecules for infection. To investigate if certain HLA-DQ alleles are associated with EBV seronegativity, we recruited ~3,300 healthy adult blood donors, identified 106 EBV-seronegative individuals, and randomly selected a control group of EBV-seropositive donors from the donor pool. A larger than expected proportion of EBV-seronegative subjects were HLA-DQ β1 *04/*05 and *06/*06, and to a lesser extent, *02/*03, compared with the control group, while a larger than expected portion of EBV-seropositive persons were HLA-DQ β1 *02/*02. We examined the ability of EBV gp42 to bind to different HLA-DQ molecules using human and mouse cells stably expressing these alleles. EBV gp42 bound less effectively to cells expressing HLA-DQ β1 *04/*05, *06/*06, or *03/*03 than to cells expressing HLA-DQ β1 *02/*02. These data are consistent with our observations of increased EBV seronegativity with DQ β1 *04/*05 or *06/*06 alleles. These findings emphasize the importance of a single genetic locus (HLA-DQ β1) to influence infectivity with EBV.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Longnecker R, Kieff E, Cohen JI. Epstein-Barr Virus. In: Knipe DM, et al., eds. Fields Virology. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2013:1898–1959.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

