The human brain produces fructose from glucose
- PMID: 28239653
- PMCID: PMC5313070
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.90508
The human brain produces fructose from glucose
Abstract
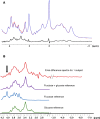
Fructose has been implicated in the pathogenesis of obesity and type 2 diabetes. In contrast to glucose, CNS delivery of fructose in rodents promotes feeding behavior. However, because circulating plasma fructose levels are exceedingly low, it remains unclear to what extent fructose crosses the blood-brain barrier to exert CNS effects. To determine whether fructose can be endogenously generated from glucose via the polyol pathway (glucose → sorbitol → fructose) in human brain, 8 healthy subjects (4 women/4 men; age, 28.8 ± 6.2 years; BMI, 23.4 ± 2.6; HbA1C, 4.9% ± 0.2%) underwent 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy scanning to measure intracerebral glucose and fructose levels during a 4-hour hyperglycemic clamp (plasma glucose, 220 mg/dl). Using mixed-effects regression model analysis, intracerebral glucose rose significantly over time and differed from baseline at 20 to 230 minutes. Intracerebral fructose levels also rose over time, differing from baseline at 30 to 230 minutes. The changes in intracerebral fructose were related to changes in intracerebral glucose but not to plasma fructose levels. Our findings suggest that the polyol pathway contributes to endogenous CNS production of fructose and that the effects of fructose in the CNS may extend beyond its direct dietary consumption.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA021984/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000140/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD010613/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK109284/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS087568/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK020495/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR001862/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U2C DK059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

