Flow virometric sorting and analysis of HIV quasispecies from plasma
- PMID: 28239654
- PMCID: PMC5313071
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.90626
Flow virometric sorting and analysis of HIV quasispecies from plasma
Abstract
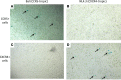
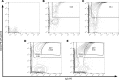
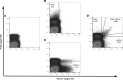
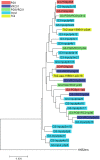
Flow cytometry is utilized extensively for cellular analysis, but technical limitations have prevented its routine application for characterizing virus. The recent introduction of nanoscale fluorescence-activated cytometric cell sorting now allows analysis of individual virions. Here, we demonstrate staining and sorting of infectious HIV. Fluorescent antibodies specific for cellular molecules found on budding virions were used to label CCR5-tropic Bal HIV and CXCR4-tropic NL4.3 HIV Env-expressing pseudovirions made in THP-1 cells (monocyte/macrophage) and H9 cells (T cells), respectively. Using a flow cytometer, we resolved the stained virus beyond isotype staining and demonstrated purity and infectivity of sorted virus populations on cells with the appropriate coreceptors. We subsequently sorted infectious simian/human immunodeficiency virus from archived plasma. Recovery was approximately 0.5%, but virus present in plasma was already bound to viral-specific IgG generated in vivo, likely contributing to the low yield. Importantly, using two broadly neutralizing HIV antibodies, PG9 and VRC01, we also sorted virus from archived human plasma and analyzed the sorted populations genetically and by proteomics, identifying the quasispecies present. The ability to sort infectious HIV from clinically relevant samples provides material for detailed molecular, genetic, and proteomic analyses applicable to future design of vaccine antigens and potential development of personalized treatment regimens.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures



References
-
- Loret S, El Bilali N, Lippé R. Analysis of herpes simplex virus type I nuclear particles by flow cytometry. Cytometry A. 2012;81(11):950–959. - PubMed
-
- Steen HB. Flow cytometer for measurement of the light scattering of viral and other submicroscopic particles. Cytometry A. 2004;57(2):94–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

