Seroprevalence of Rift Valley fever in cattle along the Akagera-Nyabarongo rivers, Rwanda
- PMID: 28240033
- PMCID: PMC6138214
- DOI: 10.4102/jsava.v88i0.1379
Seroprevalence of Rift Valley fever in cattle along the Akagera-Nyabarongo rivers, Rwanda
Abstract
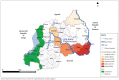
Rift Valley fever (RVF) virus is caused by a zoonotic arbovirus that is endemic to eastern and southern Africa. It has also been reported in West and North Africa, Madagascar and the Arabian Peninsula. The virus is transmitted by mosquitoes, but people can also become infected while handling blood or other body fluids of animals and humans with RVF. In 2007, there was a large outbreak of RVF in Kenya, Tanzania, Sudan and Somalia. Outbreaks were also reported in South Africa in 2008-2011. The epidemiology of RVF and factors for disease occurrence in Rwanda are neither clear nor documented. Therefore, we conducted a crosssectional study from December 2012 to March 2013 to generate baseline information on RVF in cattle. Purposive sampling of cattle (n = 595) was done in six districts, and serum samples were screened with competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). We performed a statistical analysis on the generated data, and risk factors associated with RVF seroprevalence were determined by a simple logistic regression. Overall, RVF seroprevalence was 16.8% (95% confidence interval [CI] [13.8% - 20.0%]). The highest seroprevalence was recorded in Kirehe district (36.9%) followed by Ngoma (22.3%), and the least was recorded in Nyagatare (7.9%). RVF was more likely to occur in adult cattle (19.9% [odds ratio {OR} = 1.88, 95% CI {0.98-3.61}]) compared to young cattle (10.5% [OR = 0.47, 95% CI {0.26-0.83}]). Pure exotic or cross-breeds were significantly exposed to RVF virus (seroprevalence 22.9% [OR = 4.26, 95% CI {1.82-9.99}]) in comparison to 14.1% (OR = 0.55, 95% CI [0.35-0.86]) in local breeds. Sex differences were not statistically significant. These findings indicated that cattle have been exposed to RVF virus in six districts in Rwanda with a significant risk in adult, exotic or cross-breeds in Kirehe district.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources