Antitumor activity of intratracheal inhalation of temozolomide (TMZ) loaded into gold nanoparticles and/or liposomes against urethane-induced lung cancer in BALB/c mice
- PMID: 28240047
- PMCID: PMC8240981
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2016.1247924
Antitumor activity of intratracheal inhalation of temozolomide (TMZ) loaded into gold nanoparticles and/or liposomes against urethane-induced lung cancer in BALB/c mice
Abstract
The current study aimed to develop gold nanoparticles (GNPs) and liposome-embedded gold nanoparticles (LGNPs) as drug carriers for temozolomide (TMZ) and investigate the possible therapeutic effects of intratracheal inhalation of nanoformulation of TMZ-loaded gold nanoparticles (TGNPs) and liposome-embedded TGNPs (LTGNPs) against urethane-induced lung cancer in BALB/c mice. Physicochemical characters and zeta potential studies for gold nanoparticles (GNPs) and liposome-embedded gold nanoparticles (LGNPs) were performed. The current study was conducted by inducing lung cancer chemically via repeated exposure to urethane in BALB/C mice. GNPs and LGNPs were exhibited in uniform spherical shape with adequate dispersion stability. GNPs and LGNPs showed no significant changes in comparison to control group with high safety profile, while TGNPs and LTGNPs succeed to improve all biochemical data and histological patterns. GNPs and LGNPs are promising drug carriers and succeeded in the delivery of small and efficient dose of temozolomide in treatment lung cancer. Antitumor activity was pronounced in animal-treated LTGNPs, these effects may be due to synergistic effects resulted from combination of temozolomide and gold nanoparticles and liposomes that may improve the drug distribution and penetration.
Keywords: Intratracheal inhalation; chemotherapy; gold nanoparticles; liposomes; temozolomide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Figures
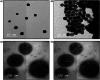


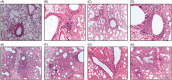
Similar articles
-
Determination of an optimal dosing schedule for combining Irinophore C™ and temozolomide in an orthotopic model of glioblastoma.J Control Release. 2015 Dec 28;220(Pt A):348-357. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.10.053. Epub 2015 Nov 1. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 26528901
-
Efficacy of Temozolomide-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticle Photothermal Therapy of Drug-Resistant Glioblastoma and Its Mechanism Study.Mol Pharm. 2022 Apr 4;19(4):1219-1229. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00083. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Mol Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35262365
-
Vincristine and temozolomide combined chemotherapy for the treatment of glioma: a comparison of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for dual drugs delivery.Drug Deliv. 2016 Oct;23(8):2720-2725. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2015.1058434. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26203691
-
Role of temozolomide in pediatric brain tumors.Childs Nerv Syst. 2006 Jul;22(7):652-61. doi: 10.1007/s00381-006-0081-z. Epub 2006 Mar 25. Childs Nerv Syst. 2006. PMID: 16565851 Review.
-
Polymeric and small molecule-conjugates of temozolomide as improved therapeutic agents for glioblastoma multiforme.J Control Release. 2022 Oct;350:494-513. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.08.024. Epub 2022 Sep 1. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35985493 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of major parameters of nanoparticles on their physical and chemical properties and recent application of nanodrug delivery system in targeted chemotherapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Nov 28;12:8483-8493. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S148359. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 29238188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unboxing the molecular modalities of mutagens in cancer.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Sep;29(41):62111-62159. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16726-w. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 34611806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hybrid Nanosystems for Biomedical Applications.ACS Nano. 2021 Feb 23;15(2):2099-2142. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c09382. Epub 2021 Jan 26. ACS Nano. 2021. PMID: 33497197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary Delivery of Anticancer Drugs via Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for the Treatment of Lung Cancer: An Update.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Jul 27;14(8):725. doi: 10.3390/ph14080725. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tailoring of Retinyl Palmitate-Based Ethosomal Hydrogel as a Novel Nanoplatform for Acne Vulgaris Management: Fabrication, Optimization, and Clinical Evaluation Employing a Split-Face Comparative Study.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jun 24;16:4251-4276. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S301597. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34211271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bancroft JD, Gamble M. (2008). Theory and practice of histological techniques. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier Health Sciences
-
- Bernert H, Sekikawa K, Radcliffe RA, et al. . (2003). Tnfa and Il-10 deficiencies have contrasting effects on lung tumor susceptibility: gender-dependent modulation of IL-10 haploinsufficiency . Mol Carcinog 38:117–23 - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya R, Patra CR, Verma R, et al. . (2007). Gold nanoparticles inhibit the proliferation of multiple myeloma cells. Adv Mat 19:711–16
-
- Bivas-Benita M, Zwier R, Junginger HE, et al. . (2005). Non-invasive pulmonary aerosol delivery in mice by the endotracheal route. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 61:214–18 - PubMed
-
- Broughton-Head VJ, Smith JR, Shur J, et al. . (2007). Actin limits enhancement of nanoparticle diffusion through cystic fibrosis sputum by mucolytics. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 20:708–17 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
