A multicenter study to define sarcopenia in patients with end-stage liver disease
- PMID: 28240805
- PMCID: PMC5762612
- DOI: 10.1002/lt.24750
A multicenter study to define sarcopenia in patients with end-stage liver disease
Abstract
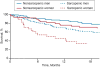
Sarcopenia is associated with increased wait-list mortality, but a standard definition is lacking. In this retrospective study, we sought to determine the optimal definition of sarcopenia in end-stage liver disease (ESLD) patients awaiting liver transplantation (LT). Included were 396 patients newly listed for LT in 2012 at 5 North American transplant centers. All computed tomography scans were read by 2 individuals with interobserver correlation of 98%. Using image analysis software, the total cross-sectional area (cm2 ) of abdominal skeletal muscle at the third lumbar vertebra was measured. The skeletal muscle index (SMI), which normalizes muscle area to patient height, was then calculated. The primary outcome was wait-list mortality, defined as death on the waiting list or removal from the waiting list for reasons of clinical deterioration. Sex-specific potential cutoff values to define sarcopenia were determined with a grid search guided by log-rank test statistics. Optimal search methods identified potential cutoffs to detect survival differences between groups. The overall median SMI was 47.6 cm2 /m2 : 50.0 in men and 42.0 in women. At a median of 8.8 months follow-up, mortality was 25% in men and 36% in women. Patients who died had lower SMI than those who survived (45.6 versus 48.5 cm2 /m2 ; P < 0.001), and SMI was associated with wait-list mortality (hazard ratio, 0.95; P < 0.001). Optimal search method yielded SMI cutoffs of 50 cm2 /m2 for men and 39 cm2 /m2 for women; these cutoff values best combined statistical significance with a sufficient number of events to detect survival differences between groups. In conclusion, we recommend that an SMI < 50 cm2 /m2 for men and < 39 cm2 /m2 for women be used to define sarcopenia in patients with ESLD awaiting LT. Liver Transplantation 23 625-633 2017 AASLD.
© 2017 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
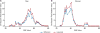
References
-
- Durand F, Buyse S, Francoz C, Laouénan C, Bruno O, Belghiti J, et al. Prognostic value of muscle atrophy in cirrhosis using psoas muscle thickness on computed tomography. J Hepatol. 2014;60:1151–1157. - PubMed
-
- Meza-Junco J, Montano-Loza AJ, Baracos VE, Prado CM, Bain VG, Beaumont C, et al. Sarcopenia as a prognostic index of nutritional status in concurrent cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;47:861–870. - PubMed
-
- Montano-Loza AJ, Meza-Junco J, Prado CM, Lieffers JR, Baracos VE, Bain VG, Sawyer MB. Muscle wasting is associated with mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10:166–173. - PubMed
-
- Tandon P, Ney M, Irwin I, Ma MM, Gramlich L, Bain VG, et al. Severe muscle depletion in patients on the liver transplant wait list: its prevalence and independent prognostic value. Liver Transpl. 2012;18:1209–1216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

