Differential Sensitivity of Target Genes to Translational Repression by miR-17~92
- PMID: 28241004
- PMCID: PMC5348049
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006623
Differential Sensitivity of Target Genes to Translational Repression by miR-17~92
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are thought to exert their functions by modulating the expression of hundreds of target genes and each to a small degree, but it remains unclear how small changes in hundreds of target genes are translated into the specific function of a miRNA. Here, we conducted an integrated analysis of transcriptome and translatome of primary B cells from mutant mice expressing miR-17~92 at three different levels to address this issue. We found that target genes exhibit differential sensitivity to miRNA suppression and that only a small fraction of target genes are actually suppressed by a given concentration of miRNA under physiological conditions. Transgenic expression and deletion of the same miRNA gene regulate largely distinct sets of target genes. miR-17~92 controls target gene expression mainly through translational repression and 5'UTR plays an important role in regulating target gene sensitivity to miRNA suppression. These findings provide molecular insights into a model in which miRNAs exert their specific functions through a small number of key target genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
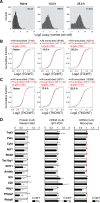
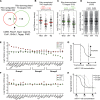
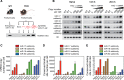
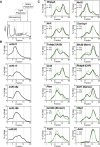

Similar articles
-
Sequence-based analysis of 5'UTR and coding regions of CASP3 in terms of miRSNPs and SNPs in targetting miRNAs.Comput Biol Chem. 2016 Jun;62:70-4. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Comput Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27107179
-
Differential TGFβ pathway targeting by miR-122 in humans and mice affects liver cancer metastasis.Nat Commun. 2016 Mar 18;7:11012. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11012. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 26987776 Free PMC article.
-
miR-106b aberrantly expressed in a double transgenic mouse model for Alzheimer's disease targets TGF-β type II receptor.Brain Res. 2010 Oct 21;1357:166-74. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.08.023. Epub 2010 Aug 13. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20709030
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Recent insights and novel bioinformatics tools to understand the role of microRNAs binding to 5' untranslated region.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Dec 27;14(1):480-95. doi: 10.3390/ijms14010480. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23271365 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NACC2, a molecular effector of miR-132 regulation at the interface between adult neurogenesis and Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 10;14(1):21163. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72096-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39256511 Free PMC article.
-
The high expression of miR-31 in lung adenocarcinoma inhibits the malignancy of lung adenocarcinoma tumor stem cells.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Aug 30;28:101122. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101122. eCollection 2021 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 34485716 Free PMC article.
-
Non-conserved microRNAs and their roles in plants: the case for legumes.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2025 Jun;27(4):450-460. doi: 10.1111/plb.70027. Epub 2025 May 1. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2025. PMID: 40311108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Development and Function of Regulatory T Cells - Lessons for a Better Understanding of MicroRNA Biology.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 9;11:2185. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02185. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MicroRNA Family Both in Normal Development and in Different Diseases: The miR-17-92 Cluster.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Feb 3;2019:9450240. doi: 10.1155/2019/9450240. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30854399 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;75(5):855–62. Epub 1993/12/03. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75(5):843–54. Epub 1993/12/03. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

