Cytokines and microbicidal molecules regulated by IL-32 in THP-1-derived human macrophages infected with New World Leishmania species
- PMID: 28241012
- PMCID: PMC5344527
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005413
Cytokines and microbicidal molecules regulated by IL-32 in THP-1-derived human macrophages infected with New World Leishmania species
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-32 (IL-32) is expressed in lesions of patients with American Tegumentary Leishmaniasis (ATL), but its precise role in the disease remains unknown.
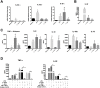
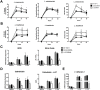
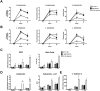
Methodology/principal findings: In the present study, silencing and overexpression of IL-32 was performed in THP-1-derived macrophages infected with Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis or L. (Leishmania) amazonensis to investigate the role of IL-32 in infection. We report that Leishmania species induces IL-32γ, and show that intracellular IL-32γ protein production is dependent on endogenous TNFα. Silencing or overexpression of IL-32 demonstrated that this cytokine is closely related to TNFα and IL-8. Remarkably, the infection index was augmented in the absence of IL-32 and decreased in cells overexpressing this cytokine. Mechanistically, these effects can be explained by nitric oxide cathelicidin and β-defensin 2 production regulated by IL-32.
Conclusions: Thus, endogenous IL-32 is a crucial cytokine involved in the host defense against Leishmania parasites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Heinhuis B, Netea MG, van den Berg WB, Dinarello CA., Joosten LAB. Interleukin-32: A predominantly intracellular proinflammatory mediator that controls cell activation and cell death. Cytokine. Elsevier Ltd; 2012;60: 321–327. - PubMed
-
- Kim S-H, Han S-Y, Azam T, Yoon D-Y, Dinarello CA. Interleukin-32. Immunity. 2005;22: 131–142. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

