Nematode neuropeptides as transgenic nematicides
- PMID: 28241060
- PMCID: PMC5344539
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006237
Nematode neuropeptides as transgenic nematicides
Abstract
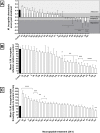
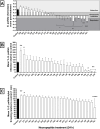
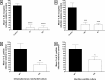
Plant parasitic nematodes (PPNs) seriously threaten global food security. Conventionally an integrated approach to PPN management has relied heavily on carbamate, organophosphate and fumigant nematicides which are now being withdrawn over environmental health and safety concerns. This progressive withdrawal has left a significant shortcoming in our ability to manage these economically important parasites, and highlights the need for novel and robust control methods. Nematodes can assimilate exogenous peptides through retrograde transport along the chemosensory amphid neurons. Peptides can accumulate within cells of the central nerve ring and can elicit physiological effects when released to interact with receptors on adjoining cells. We have profiled bioactive neuropeptides from the neuropeptide-like protein (NLP) family of PPNs as novel nematicides, and have identified numerous discrete NLPs that negatively impact chemosensation, host invasion and stylet thrusting of the root knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita and the potato cyst nematode Globodera pallida. Transgenic secretion of these peptides from the rhizobacterium, Bacillus subtilis, and the terrestrial microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii reduce tomato infection levels by up to 90% when compared with controls. These data pave the way for the exploitation of nematode neuropeptides as a novel class of plant protective nematicide, using novel non-food transgenic delivery systems which could be deployed on farmer-preferred cultivars.
Conflict of interest statement
Queen's University Belfast are in the process of submitting a patent application covering aspects of the data presented within this manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Nicol JM, Stirling GR, Turner SJ, Coyne DL, de Nijs L, Hockland S, Maafi ZT. Current nematode threats to world agriculture Genomics and Molecular Genetics of Plant-Nematode Interactions (Jones JT, Gheysen G, Fenoll C., eds). Heidelberg: Springer; 2011; pp. 21–44
-
- Council of the European Union. 1991. Council Directive 91/414/EEC of 15 July 1991 concerning the placing of plant protection products on the market. Official Journal. 2005; L 230: 1–32.
-
- UNEP. Montreal protocol on substances that deplete the ozone layer. 2014 report of the methyl bromide technical options committee. 2015; p 13. ISBN: 978-9966-076-08-3.
-
- Babich H, Davis DL, Stotzky G. Dibromochloropropane (DBCP): a review. The Science of Total Environment. 1981; 17: 207–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

