Plasma exchange for Guillain-Barré syndrome
- PMID: 28241090
- PMCID: PMC6464100
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001798.pub3
Plasma exchange for Guillain-Barré syndrome
Abstract
Background: Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is an acute paralysing disease caused by peripheral nerve inflammation. This is an update of a review first published in 2001 and last updated in 2012.
Objectives: To assess the effects of plasma exchange for treating GBS.
Search methods: On 18 January 2016 we searched the Cochrane Neuromuscular Specialised Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, and Embase. We also searched clinical trials registries.
Selection criteria: Randomised and quasi-randomised trials of plasma exchange versus sham exchange or supportive treatment, or comparing different regimens or techniques of plasma exchange.
Data collection and analysis: We followed standard Cochrane methodology.
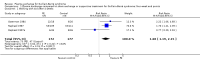
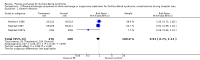
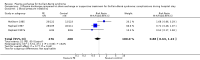
Main results: In the first version of this review there were six eligible trials concerning 649 participants comparing plasma exchange with supportive treatment. No new eligible trials have been identified in subsequent updates. Two other studies compared different numbers of plasma exchanges. Overall the included trials had a moderate risk of bias (in general, the studies were at low risk but all had a high risk of bias from lack of blinding).In one trial with 220 severely affected participants, the median time to recover walking with aid was significantly shorter with plasma exchange (30 days) than without plasma exchange (44 days). In another trial with 91 mildly affected participants, the median time to onset of motor recovery was significantly shorter with plasma exchange (six days) than without plasma exchange (10 days). After four weeks, moderate-quality evidence from the combined data of three trials accounting for a total of 349 patients showed that plasma exchange significantly increased the proportion of patients who recovered the ability to walk with assistance (risk ratio (RR) 1.60, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.19 to 2.15).In five trials with 623 participants in total, moderate-quality evidence showed that the RR for improvement by one or more disability grades after four weeks was 1.64 (95% CI 1.37 to 1.96) times greater with plasma exchange. Participants treated with plasma exchange also fared better, according to moderate-quality evidence, in time to recover walking without aid (three trials with 349 participants; RR 1.72, 95% CI 1.06 to 2.79) and requirement for artificial ventilation (five trials with 623 participants; RR 0.53, 95% CI 0.39 to 0.74). More participants had relapses by the end of follow-up in the plasma exchange group than in the control group (six trials with 649 participants; RR 2.89, 95% CI 1.05 to 7.93; moderate-quality evidence). Despite this, according to moderate-quality evidence, the likelihood of full muscle strength recovery at one year was greater with plasma exchange than without plasma exchange (five trials with 404 participants; RR 1.24, 95% CI 1.07 to 1.45), and the likelihood of severe motor sequelae was less (six trials with 649 participants; RR 0.65, 95% CI 0.44 to 0.96). High-quality evidence from six trials with 649 participants could not confirm or refute a lower risk of death following plasma exchange compared to control (RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.45 to 1.65).Three trials (N = 556) provided details of serious adverse events during the hospital stay; combined analyses found no increase in serious infectious events compared to the control group (RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.13), nor were there clear differences in blood pressure instability, cardiac arrhythmias or pulmonary emboli.
Authors' conclusions: Moderate-quality evidence shows significantly more improvement with plasma exchange than with supportive care alone in adults with Guillain-Barré syndrome, without a significant increase in serious adverse events. According to moderate-quality evidence, there was a small but significant increase in the risk of relapse during the first six to 12 months after onset in people treated with plasma exchange compared with those who were not treated. Despite this, after one year, full recovery of muscle strength was more likely and severe residual weakness less likely with plasma exchange.
Conflict of interest statement
SC co‐ordinated two RCTs that reported a beneficial effect. She has no known commercial conflicts of interest.
RACH holds or held consultancies with the following companies that produce IVIg or immunosuppressive drugs: CSL Behring, LFB, and Novartis. He participated in an RCT that did not report any beneficial effect and co‐ordinated another that showed equivalent efficacy of plasma exchange and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg).
DA: no known conflicts of interest.
Figures

















Update of
-
Plasma exchange for Guillain-Barré syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jul 11;(7):CD001798. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001798.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 27;2:CD001798. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001798.pub3. PMID: 22786475 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Farkkila 1987 {published data only}
-
- Färkkilä M, Kinnunen E, Haapanen E, Livanainen M. Guillain Barré syndrome: quantitative measurement of plasma exchange therapy. Neurology 1987;37(5):837‐40. [PUBMED: 3553986] - PubMed
Greenwood 1984 {published data only}
-
- Greenwood RJ, Newsom‐Davis J, Hughes RAC, Aslan S, Bowden AN, Chadwick DW, et al. Controlled trial of plasma exchange in acute inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy. Lancet 1984;1(8382):877‐9. [PUBMED: 6143188] - PubMed
McKhann 1985 {published data only}
-
- The Guillain‐Barré syndrome study group. Plasmapheresis and acute Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Neurology 1985;35(8):1096‐104. [PUBMED: 4022342] - PubMed
Osterman 1984 {published data only}
-
- Osterman PO, Fagius J, Lundemo G, Pihlstedt P, Pirskanen R, Siden A, et al. Beneficial effects of plasma exchange in acute inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy. Lancet 1984;2(8415):1296‐9. [PUBMED: 6150321] - PubMed
Raphaël 1987 {published data only}
-
- French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Efficiency of plasma exchange in Guillain‐Barré syndrome: role of replacement fluids. Annals of Neurology 1987;22(6):753‐61. [PUBMED: 2893583] - PubMed
-
- French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Plasma exchange in Guillain‐Barré syndrome: one year follow‐up. Annals of Neurology 1992;32(1):94‐7. [PUBMED: 1642477] - PubMed
Raphaël 1997a {published data only}
-
- French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain‐Barré Syndrome. Appropriate number of plasma exchanges in Guillain‐Barré Syndrome. Annals of Neurology 1997;41(3):298‐306. [PUBMED: 9066350] - PubMed
Raphaël 1997b {published and unpublished data}
-
- French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain‐Barré Syndrome. Appropriate number of plasma exchanges in Guillain‐Barré Syndrome. Annals of Neurology 1997;41(3):298‐306. [PUBMED: 9066350] - PubMed
Raphaël 1997c {published and unpublished data}
-
- French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain‐Barré Syndrome. Appropriate number of plasma exchanges in Guillain‐Barré Syndrome. Annals of Neurology 1997;41(3):298‐306. [PUBMED: 9066350] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
de‐Zoysa 1994 {published data only}
-
- de‐Zoysa NS, Jayaweera KK, Vaithianathan T. Manual plasmapheresis in the treatment of Guillain Barré syndrome. Journal of Clinical Apheresis 1994;9(2):147‐50. - PubMed
El Bayoumi 2011 {published data only}
Mendell 1985 {published data only}
-
- Mendell JR, Kissel JT, Kennedy MS, Sahenk Z, Grinvalsky HT, Pittman GL, et al. Plasma exchange and prednisone in Guillain‐Barré syndrome: a controlled randomised trial. Neurology 1985;35(11):1551‐5. - PubMed
Morosetti 1994 {published data only}
-
- Morosetti M, Meloni C, Taccone Gallucci M, Rossini PM, Felicioni R, Palombo G, et al. Plasmapheresis versus plasma perfusion in acute Guillain‐Barré syndrome. ASAIO Journal 1994;40(3):M638‐42. - PubMed
Rock 1997 {published data only}
-
- Rock G. Pentastarch instead of albumin as replacement fluid for therapeutic plasma exchange. The Canadian Apheresis Group. Journal of Clinical Apheresis 1997;12(4):165‐9. - PubMed
Wollinsky 2001 {published data only}
-
- Wollinsky KH, Hulser PJ, Brinkmeier H, Aulkemeyer P, Bossenecker W, Huber‐Hartmann KH, et al. CSF filtration is an effective treatment of Guillain Barré syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Neurology 2001;57(5):774‐80. - PubMed
Additional references
Asbury 1990
-
- Asbury AK, Cornblath DR. Assessment of current diagnostic criteria for Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Annals of Neurology 1990;27 Suppl:S21‐4. - PubMed
Bouget 1993
-
- Bouget J, Chevret S, Chastang C, Raphael JC. Plasma exchange morbidity in Guillain Barré syndrome: results from the French prospective, randomized, multicenter study. The French Cooperative Group. Critical Care Medicine 1993;21(5):651‐8. - PubMed
Brettle 1978
-
- Brettle RP, Gross M, Legg NJ, Lockwood M, Pallis C. Treatment of acute polyneuropathy by plasma exchange. Lancet 1978;2(8099):1100. - PubMed
Consensus 1986
-
- Consensus Conference. The utility of therapeutic plasmapheresis for neurological disorders. Journal of the American Medical Association 1986;256(10):1333‐7. - PubMed
Cook 1971
-
- Cook SD, Dowling PC, Murray MR, Whitaker JN. Circulating demyelinating factors in acute idiopathic polyneuropathy. Archives of Neurology 1971;24(2):136‐44. - PubMed
Cortese 2011
Espérou 2000
-
- Espérou H, Jars Guincestre MC, Bolgert F, Raphael JC, Durand‐Zaleski I, and the French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Cost‐effectiveness of plasma exchange therapy for the treatment of Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Intensive Care Medicine 2000;26(8):1094‐100. - PubMed
Farkkila 1992
-
- Farkkila M, Penttila P. Plasma exchange therapy reduces the nursing care needed in Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Journal of Advanced Nursing 1992;17(6):672‐5. - PubMed
GRADEpro 2008 [Computer program]
-
- Jan Brozek, Andrew Oxman, Holger Schünemann. GRADEpro. Version 3.2 for Windows. Jan Brozek, Andrew Oxman, Holger Schünemann, 2008.
Harrison 1984
-
- Harrison BM, Hansen LA, Pollard JD, Leod JG. Demyelination induced by serum from patients with Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Annals of Neurology 1984;15(2):163‐70. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hughes 1978
-
- Hughes RAC, Newsom‐Davis JM, Perkin GD, Pierce JM. Controlled trial of prednisolone in acute polyneuropathy. Lancet 1978;2(8104‐5):750‐3. - PubMed
Hughes 2007
-
- Hughes RA, Swan AV, Raphael JC, Annane D, Van Koningsveld, Doorn PA. Immunotherapy for Guillain‐Barré syndrome: a systematic review. Brain 2007;130(Pt 9):2245‐57. - PubMed
Hughes 2011
Hughes 2014
Mark 1980
-
- Mark B, Hurwitz J, Olanow CW, Fay JW. Plasmapheresis in idiopathic inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy. Neurology 1980;30(4):361.
McKhann 1985b
-
- The Guillain‐Barré Syndrome Study Group. The North American study of plasmapheresis in the Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Journal of Clinical Apheresis 1985;2:315‐20. - PubMed
McKhann 1988
-
- McKhann GM, Griffin JW, Cornblath DR, Mellits ED, Fisher RS, Quaskey SA, et al. Plasmapheresis and Guillain‐Barré syndrome: analysis of prognostic factors and the effect of plasmapheresis. Annals of Neurology 1988;23(4):347‐53. - PubMed
Mendell 1985b
-
- Mendell JR, Kissel JT, Kennedy MS, Sahenk Z, Grinvalsky HT, Pittman GL, et al. Plasma exchange and prednisone in acute inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy: a controlled randomized trial. Journal of Clinical Apheresis 1985;2(4):332‐42. - PubMed
Metral 1989
-
- Metral S, Raphaël JC, Hort‐Legrand CL, Elkharrat D. Serum demyelinating activity and Guillain‐Barre syndrome: favorable effect of plasma exchange [Activité démyélinisante sérique et syndrome de Guillain‐Barré: effet favorable des échanges plasmatiques]. Revue Neurologique 1989;145(4):312‐9. - PubMed
PSGBS Group 1997
-
- Plasma Exchange/Sandoglobulin Guillain‐Barré Syndrome Trial Group. Randomised trial of plasma exchange, intravenous immunoglobulin, and combined treatments in Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Lancet 1997;349(9047):225‐30. - PubMed
Raphaël 1985
-
- Raphael JC, Chastang C, and the Cooperative French Group. Cooperative randomized trial of plasma exchange in Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Plasma Therapy and Transfusion Technology 1985;6:603‐4.
Raphaël 1986
-
- Raphael JC, Chastang C. Cooperative randomized trial of plasma exchange in the Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Short term effects and comparison of diluted albumin and fresh frozen plasma. Life Support System 1986;4:329‐31.
Raphaël 1992
-
- French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Plasma exchange in Guillain‐Barré syndrome: one‐year follow‐up. Annals of Neurology 1992;32(1):94‐7. - PubMed
Raphaël 1996
-
- Raphaël JC, Chevret S, Jars‐Guincestre MC, Chastang C, Gajdos PH. Treatment of Guillain‐Barré syndrome by plasma exchange: proposal of a therapeutic strategy [Traitement du syndrome de Guillain‐Barré par les échanges plasmatiques: proposition d’une stratégie thérapeutique]. Revue Neurologique 1996;152(5):359‐64. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Ropper 1980
-
- Ropper AH, Shahani B, Huggins CE. Improvement in four patients with acute Guillain‐Barré syndrome after plasma exchange. Neurology 1980;30:361.
Schooneman 1981
-
- Schooneman F, Janot C, Streiff F, Gérard A, Dureux JB, Canton P, et al. Plasma exchange in Guillain‐Barré syndrome ten cases. Plasmapheresis Therapy 1981;2:117‐21.
Shumak 1984
-
- Shumak KH, Rock GA. Therapeutic plasma exchange. New England Journal of Medicine 1984;310(1212):762‐71. - PubMed
Sumner 1982
-
- Sumner A, Said G, Idy I, Metral S. Electrophysiological and morphological effects of the injection of Guillain‐Barré sera in the sciatic nerve of the rat [Syndrome de Guillain‐Barré. Effects electro‐physiologiques du sérum humain introduit dans l'espace endoneural du nerf sciatique du rat. Résultats préliminaires]. Revue Neurologique 1982;138(1):17‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Valbonesi 1981
-
- Valbonesi M, Garelli S, Mosconi L, Zerbi D, Celano I. Plasma exchange as a therapy for Guillain‐Barré syndrome with immune complexes. Vox Sanguinis 1981;41:74‐8. - PubMed
Van der Meché 1992
-
- Meché FGA, Schmitz PIM, Dutch Guillain‐Barré Study Group. A randomized trial comparing intravenous immune globulin and plasma exchange in Guillain‐Barré syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 1992;326(17):1123‐9. - PubMed
Visser 1999
-
- Visser LH, Schmitz PI, Meulstee J, Doorn PA, Meché FG. Prognostic factors of Guillain‐Barré syndrome after intravenous immunoglobulin or plasma exchange. Dutch Guillain‐Barré Study Group. Neurology 1999;53(3):598‐604. - PubMed
Willison 2016
-
- Willison HJ, Jacobs BC, Doorn PA. Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Lancet 2016;388:717‐27. - PubMed
Yuki 2012
-
- Yuki N, Hartung HP. Guillain‐Barré syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2012;366(24):2294‐304. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Raphael 2012
Raphaël 2001
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

