Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Suppress Phagolysosome Activation in Macrophages
- PMID: 28241314
- PMCID: PMC5341620
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.16-21082
Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Suppress Phagolysosome Activation in Macrophages
Abstract
Purpose: The eye is an immune-privileged microenvironment that has adapted several mechanisms of immune regulation to prevent inflammation. One of these potential mechanisms is retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPE) altering phagocytosis in macrophages.
Methods: The conditioned media of RPE eyecups from eyes of healthy mice and mice with experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) were used to treat primary macrophage phagocytizing pHrodo bacterial bioparticles. In addition, the neuropeptides were depleted from the conditioned media of healthy RPE eyecups and used to treat phagocytizing macrophages. The conditioned media from healthy and EAU RPE eyecups were assayed for IL-6, and IL-6 was added to the healthy conditioned media, and neutralized in the EAU conditioned media. The macrophages were treated with the conditioned media and assayed for fluorescence. The macrophages were imaged, and the fluorescence intensity, relative to active phagolysosomes, was measured. Also, the macrophages were assayed using fluorescent viability dye staining.
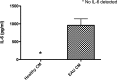
Results: The conditioned media from healthy, but not from EAU RPE eyecups suppressed phagolysosome activation. Depletion of the neuropeptides alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and neuropeptide Y from the healthy RPE eyecup conditioned media resulted in macrophage death. In the EAU RPE eyecup conditioned media was 0.96 ± 0.18 ng/mL of IL-6, and when neutralized the conditioned media suppressed phagolysosome activation.
Conclusions: The healthy RPE through soluble molecules, including alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and neuropeptide Y, suppresses the activation of the phagolysosome in macrophages. In EAU, the IL-6 produced by the RPE promotes the activation of phagolysosomes in macrophages. These results demonstrate that under healthy conditions, RPE promotes an altered pathway of phagocytized material in macrophages with implications on antigen processing and clearance.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cell Line Suppression of Phagolysosome Activation.Int J Ophthalmol Eye Sci. 2015 Jan 29;Suppl 2(1):1-6. Int J Ophthalmol Eye Sci. 2015. PMID: 25905107 Free PMC article.
-
Melanocortin 5 Receptor Expression and Recovery of Ocular Immune Privilege after Uveitis.Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2022 May 19;30(4):876-886. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2020.1849735. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 33617397 Free PMC article.
-
The immune privileged retina mediates an alternative activation of J774A.1 cells.Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2009 Nov-Dec;17(6):380-9. doi: 10.3109/09273940903118642. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2009. PMID: 20001256 Free PMC article.
-
[Intraocular inflammation and homeostasis of the eye].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2009 Mar;113(3):344-77; discussion 378. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19348183 Review. Japanese.
-
Proliferative vitreo-retinal disorders: experimental models in vivo and in vitro.Acta Ophthalmol Suppl (1985). 1992;(201):1-63. Acta Ophthalmol Suppl (1985). 1992. PMID: 1322004 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Soluble Membranes from Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Mediate Apoptosis in Macrophages.Cells. 2021 May 13;10(5):1193. doi: 10.3390/cells10051193. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34068205 Free PMC article.
-
Melanocortin receptor agonists suppress experimental autoimmune uveitis.Exp Eye Res. 2022 May;218:108986. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.108986. Epub 2022 Feb 20. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 35196505 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral retinal avascularity and capillary leakage in central serous chorioretinopathy.J Curr Ophthalmol. 2019 Jan 30;31(2):220-224. doi: 10.1016/j.joco.2019.01.004. eCollection 2019 Jun. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31317104 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide Y Is an Immunomodulatory Factor: Direct and Indirect.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 6;11:580378. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.580378. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33123166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells in Regulation of Macrophages/Microglial Cells in Retinal Immunobiology.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 13;12:724601. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.724601. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484232 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wu GS,, Rao NA. A novel retinal pigment epithelial protein suppresses neutrophil superoxide generation. I. Characterization of the suppressive factor. Exp Eye Res. 1996; 63: 713–725. - PubMed
-
- Sugita S,, Horie S,, Nakamura O,, et al. Retinal pigment epithelium-derived CTLA-2alpha induces TGFbeta-producing T regulatory cells. J Immunol. 2008; 181: 7525–7536. - PubMed
-
- Sugita S,, Kawazoe Y,, Imai A,, Usui Y,, Takahashi M,, Mochizuki M. Suppression of IL-22-producing T helper 22 cells by RPE cells via PD-L1/PD-1 interactions. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013; 54: 6926–6933. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

