Exome Sequencing in a Family with Luminal-Type Breast Cancer Underpinned by Variation in the Methylation Pathway
- PMID: 28241424
- PMCID: PMC5343999
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18020467
Exome Sequencing in a Family with Luminal-Type Breast Cancer Underpinned by Variation in the Methylation Pathway
Abstract
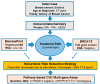
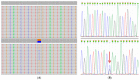
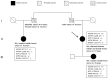
Panel-based next generation sequencing (NGS) is currently preferred over whole exome sequencing (WES) for diagnosis of familial breast cancer, due to interpretation challenges caused by variants of uncertain clinical significance (VUS). There is also no consensus on the selection criteria for WES. In this study, a pathology-supported genetic testing (PSGT) approach was used to select two BRCA1/2 mutation-negative breast cancer patients from the same family for WES. Homozygosity for the MTHFR 677 C>T mutation detected during this PSGT pre-screen step was considered insufficient to cause bilateral breast cancer in the index case and her daughter diagnosed with early-onset breast cancer (<30 years). Extended genetic testing using WES identified the RAD50 R385C missense mutation in both cases. This rare variant with a minor allele frequency (MAF) of <0.001 was classified as a VUS after exclusion in an affected cousin and extended genotyping in 164 unrelated breast cancer patients and 160 controls. Detection of functional polymorphisms (MAF > 5%) in the folate pathway in all three affected family members is consistent with inheritance of the luminal-type breast cancer in the family. PSGT assisted with the decision to pursue extended genetic testing and facilitated clinical interpretation of WES aimed at reduction of recurrence risk.
Keywords: breast cancer; exome sequencing; methylation pathway; pathology; pharmacogenomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Maritha J. Kotze is a director and shareholder of Gknowmix (Pty) Ltd. that has developed a database tool for research translation under the auspices of the South African Medical Research Council. Susan J. van Rensburg is a scientific advisor of Gknowmix, with no potential conflict of interest reported by the other authors. Maritha J. Kotze is the inventor of a South African Medical Research Council patent 2001/5419 (2 July 2001) entitled “A method of diagnosing patients with cardiovascular disease or a genetic predisposition for cardiovascular disease”. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Nordgard S.H., Alnaes G.I., Hihn B., Lingjaerde O.C., Liestøl K., Tsalenko A., Sørlie T., Lønning P.E., Børresen-Dale A.L., Kristensen V.N. Pathway based analysis of SNPs with relevance to 5-FU therapy: Relation to intratumoral mRNA expression and survival. Int. J. Cancer. 2008;123:577–585. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23541. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Babyshkina N., Malinovskaya E., Nazarenko M., Koval M., Gervas P., Potapova O., Slonimskaya E., Cherdyntseva N. The effect of folate-related SNPs on clinicopathological features, response to neoadjuvant treatment and survival in pre- and postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Gene. 2013;518:397–404. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.095. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

