The Roles of Histone Demethylase Jmjd3 in Osteoblast Differentiation and Apoptosis
- PMID: 28241471
- PMCID: PMC5372993
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm6030024
The Roles of Histone Demethylase Jmjd3 in Osteoblast Differentiation and Apoptosis
Abstract
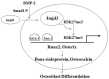
Posttranslational modifications including histone methylation regulate gene transcription through directly affecting the structure of chromatin. Trimethylation of histone 3 lysine 27 (H3K27me3) is observed at the promoters of a wide variety of important genes, especially for mammalian development, and contributes to gene silencing. Demethylase Jumonji domain-containing 3 (Jmjd3) catalyzes the transition of H3K27me3 to H3K27me1, therefore from a repressive to an active status of gene expression. Jmjd3 plays important roles in cell differentiation, inflammation, and tumorigenesis by targeting distinct transcription factors. In this review, we summarize the pivotal roles of Jmjd3 in maintaining skeletal homeostasis through regulating osteoblast differentiation, maturation, and apoptosis.
Keywords: H3K27me3; Jmjd3; bone formation; osteoblast apoptosis; osteoblast differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Luger K., Mader A.W., Richmond R.K., Sargent D.F., Richmond T.J. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1997;389:251–260. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

