The antibacterial activity of extracts of nine plant species with good activity against Escherichia coli against five other bacteria and cytotoxicity of extracts
- PMID: 28241818
- PMCID: PMC5329917
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1645-z
The antibacterial activity of extracts of nine plant species with good activity against Escherichia coli against five other bacteria and cytotoxicity of extracts
Abstract
Background: The development of antibiotic resistant bacteria stems from a number of factors, including inappropriate use of antibiotics in human and animal health and their prolonged use as growth promoters at sub-clinical doses in poultry and livestock production. We were interested in investigating plants that could be useful in protecting humans or animals against diarrhoea. We decided to work on extracts of nine plant species with good activity against Escherichia coli based on earlier work in the Phytomedicine Programme. Leaves of nine medicinal plant species with high antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli were extracted with acetone and their minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) values determined using a microplate serial dilution technique against Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis and Bacillus cereus) and Gram-negative (Escherichia coli, Salmonella Typhimurium and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) bacteria. Bioautography was used to determine the number of bioactive compounds in each extract. In vitro safety of the extracts was determined using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazolyl-2)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide reduction assay on Vero cells.
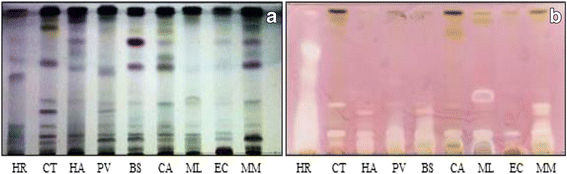
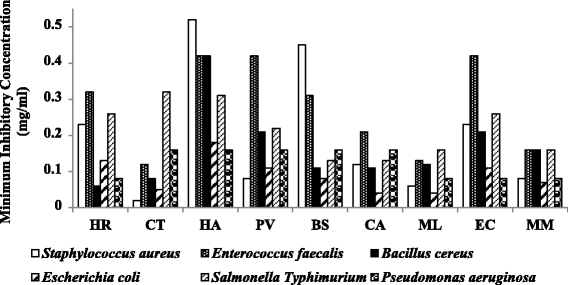
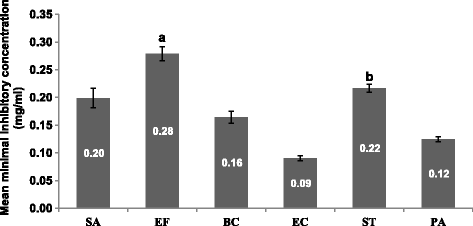
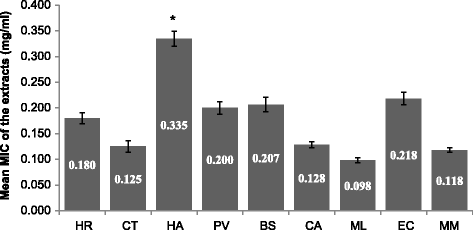
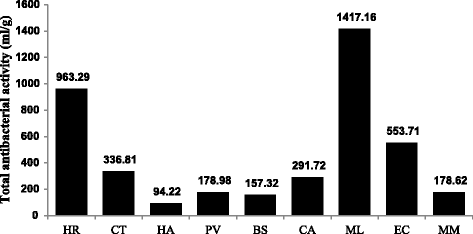
Results: The extracts were active against all the pathogens with average MICs ranging from 0.02 to 0.52 mg/ml. As expected E. coli was relatively sensitive, while E. faecalis and S. Typhimurium were more resistant to the extracts (average MICs of 0.28 mg/ml and 0.22 mg/ml respectively). Cremaspora triflora and Maesa lanceolata leaf extracts had higher activity than the other extracts against Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens with mean MICs of 0.07 mg/ml and 0.09 mg/ml respectively. Extracts of Maesa lanceolata and Hypericum roeperianum had the highest total antibacterial activity (TAA) at 1417 and 963 ml/g respectively. All extracts with the exception of that of Maesa lanceolata, Elaeodendron croceum and Calpurnia aurea had relatively low cytotoxicity with LC50 > 20 μg/ml. Cremaspora triflora had the best selectivity index (SI) against S. aureus and E. coli of 2.87 and 1.15 respectively. Hypericum roeperianum had a SI of 1.10 against B. cereus. Bioautography revealed 1-6 visible antimicrobial compounds that were generally non-polar.
Conclusions: There was a weak positive, but statistically non-significant correlation between the potency of the extracts and their cytotoxicity (R = 0.45, ρ > 0.05). The activity of the extracts on the test bacteria was in some cases not correlated with cytotoxicity, as shown by selectivity indices >1. This means that cellular toxicity was probably not due to compounds with antibacterial activity. Some of the extracts had a good potential for therapeutic use against the bacterial pathogens or for application in treating diarhoea. It does not appear that activity against E. coli is a good predictor of activity against Gram-negative rather than Gram-positive bacteria. Further investigation is in progress on C. triflora and H. roeperianum, both of which had promising activities and potential safety based on cytotoxicity.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Cellular safety; Correlation; Efficacy; Nosocomial bacteria; Potency.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The efficacy and safety of nine South African medicinal plants in controlling Bacillus anthracis Sterne vaccine strain.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Jan 8;16:5. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0980-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 26742484 Free PMC article.
-
Potency and selectivity indices of acetone leaf extracts of nine selected South African trees against six opportunistic Enterobacteriaceae isolates from commercial chicken eggs.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Feb 2;17(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1597-3. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28148263 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of acetone leaf extracts of nine under-investigated south African Eugenia and Syzygium (Myrtaceae) species and their selectivity indices.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Jun 20;19(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2547-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31221162 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of antimicrobial activity of Allium, Ocimum, and Thymus spp. confirms their promising application for increasing food safety.Food Res Int. 2024 Jul;188:114408. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114408. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38823853
-
Piper betle (L): Recent Review of Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties, Safety Profiles, and Commercial Applications.Molecules. 2021 Apr 16;26(8):2321. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082321. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33923576 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Phytochemicals and Bioactive Properties in Mangrove Associate Suaeda monoica Forssk. ex J.F.Gmel. of Indian Sundarbans.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 10;12:584019. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.584019. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33790782 Free PMC article.
-
ROS mediated anticandidal efficacy of 3-Bromopyruvate prevents vulvovaginal candidiasis in mice model.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 28;18(12):e0295922. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295922. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38153954 Free PMC article.
-
Hindering the formation and promoting the dispersion of medical biofilms: non-lethal effects of seagrass extracts.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 May 30;18(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2232-7. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29843708 Free PMC article.
-
Agonistic antibacterial potential of Loigolactobacillus coryniformis BCH-4 metabolites against selected human pathogenic bacteria: An in vitro and in silico approach.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 10;18(8):e0289723. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289723. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37561679 Free PMC article.
-
Large-Scale Screening of 239 Traditional Chinese Medicinal Plant Extracts for Their Antibacterial Activities against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Cytotoxic Activities.Pathogens. 2020 Mar 4;9(3):185. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9030185. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32143422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Awouafack MD, McGaw LJ, Gottfried S, Mbouangouere R, Tane P, Spiteller M, Eloff JN. Antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity of the ethanol extract, fractions and eight compounds isolated from Eriosema robustum (Fabaceae) BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013;13:1. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-289. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

