Remotely engaged: Lessons from remote monitoring in multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 28241935
- PMCID: PMC5331862
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2017.01.006
Remotely engaged: Lessons from remote monitoring in multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Objectives: Evaluate web-based patient-reported outcome (wbPRO) collection in MS subjects in terms of feasibility, reliability, adherence, and subject-perceived benefits; and quantify the impact of MS-related symptoms on perceived well-being.
Methods: Thirty-one subjects with MS completed wbPROs targeting MS-related symptoms over six months using a customized web portal. Demographics and clinical outcomes were collected in person at baseline and six months.
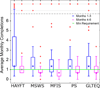
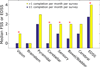
Results: Approximately 87% of subjects completed wbPROs without assistance, and wbPROs strongly correlated with standard PROs (r>0.91). All wbPROs were completed less frequently in the second three months (p<0.05). Frequent wbPRO completion was significantly correlated with higher step on the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) (p=0.026). Nearly 52% of subjects reported improved understanding of their disease, and approximately 16% wanted individualized wbPRO content. Over half (63.9%) of perceived well-being variance was explained by MS symptoms, notably depression (rs=-0.459), fatigue (rs=-0.390), and pain (rs=-0.389).
Conclusions: wbPRO collection was feasible and reliable. More disabled subjects had higher completion rates, yet most subjects failed requirements in the second three months. Remote monitoring has potential to improve patient-centered care and communication between patient and provider, but tailored PRO content and other innovations are needed to combat declining adherence.
Keywords: Multiple sclerosis; Patient empowerment; Patient engagement technology; Patient-provider communication; Patient-reported outcomes; Personalized medicine.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart M, Brown JB, Donner A, McWhinney IR, Oates J, Weston WW, Jordan J. The impact of patient-centered care on outcomes. J. Fam. Pract. 2000;49:796–804. doi: see also this commentary by Ronal Epstein; http://www.jfponline.com/Pages.asp?AID=2593&UID= - PubMed
-
- Basch E, Deal AM, Kris MG, Scher HI, Hudis CA, Sabbatini P, Rogak L, Bennett AV, Dueck AC, Atkinson TM, Chou JF, Dulko D, Sit L, Barz A, Novotny P, Fruscione M, Sloan JA, Schrag D. Symptom Monitoring With Patient-Reported Outcomes During Routine Cancer Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015;34 JCO.2015.63.0830. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertakis KD, Azari R. Patient-Centered Care is Associated with Decreased Health Care Utilization. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2011;24:229–239. - PubMed
-
- Bertakis KD, Azari R. Determinants and outcomes of patient-centered care. Patient Educ. Couns. 2011;85:46–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

