Determinants of Adiposity Rebound Timing in Children
- PMID: 28242030
- PMCID: PMC5404387
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.01.051
Determinants of Adiposity Rebound Timing in Children
Abstract
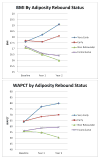
Objective: Adiposity rebound (AR) or BMI (body mass index) rebound refers to the increase in BMI following the minimum BMI in early childhood. Early AR (before age 5) is predictive of adult obesity. To determine how 4 domains - demographics, maternal BMI, food security, and behavioral characteristics - may affect timing of AR.
Study design: A total of 248 children, ages 2.5-3.5 years, in Latino farmworker families in North Carolina were examined at baseline and every 3 months for 2 years. BMI was plotted serially for each child and the onset of BMI rebound was determined by visual inspection of the graphs. Given the ages of the children, all rebounds were detected before age 5 years and were deemed "early," whereas other children were classified as "nonrebounders." Classes were then compared in terms of the 4 domains with the use of bivariate analyses and linear mixed models.
Results: A total of 131 children demonstrated early rebound, 59 children were nonrebounders, and a further 35 had inconclusive data. Parents of early rebounders were less likely to have documentation permitting legal residence in the US. Mothers of early rebounders were on average 3 BMI units heavier. Sex, household food security, diet quality, caloric intake, and daily activity did not differ between classes. In multivariable analysis, female sex, limited maternal education, increased maternal BMI, and increased caloric intake were significant predictors of early rebound.
Conclusion: High maternal BMI was the strongest predictor of early BMI rebound, but increased caloric intake also was significant. Limiting excess calories could delay premature AR and lower the risk of future obesity.
Keywords: Latino farmworker families; childhood obesity; determinants of adiposity rebound timing; diet; early adiposity rebound; food security; maternal body mass index; physical activity.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Rosado JI, Bennett Johnson S, McGinnity KA, Cuevas JP. Obesity among Latino children within a migrant farmworker community. Am J Prev Med. 2013;44:S274–81. - PubMed
-
- Kilanowski JF, Ryan-Wenger N. Health status of an invisible population: carnival and migrant worker children. West J Nurs Res. 2007;29:100–20. - PubMed
-
- Power C, Lake JK, Cole TJ. Measurement and long-term health risks of child and adolescent fatness. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1997;21:507–26. - PubMed
-
- Rolland-Cachera MF, Deheeger M, Bellisle F, Sempe M, Guilloud-Bataille, Patois E. Adiposity rebound in children: a simple indicator for predicting obesity. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984;39:129–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

