Fluorescence High-Throughput Screening for Inhibitors of TonB Action
- PMID: 28242720
- PMCID: PMC5405212
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00889-16
Fluorescence High-Throughput Screening for Inhibitors of TonB Action
Abstract
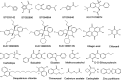
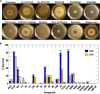
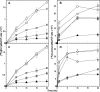
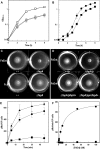
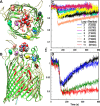
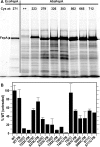
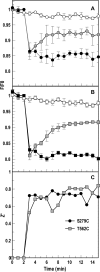
Gram-negative bacteria acquire ferric siderophores through TonB-dependent outer membrane transporters (TBDT). By fluorescence spectroscopic hgh-throughput screening (FLHTS), we identified inhibitors of TonB-dependent ferric enterobactin (FeEnt) uptake through Escherichia coli FepA (EcoFepA). Among 165 inhibitors found in a primary screen of 17,441 compounds, we evaluated 20 in secondary tests: TonB-dependent ferric siderophore uptake and colicin killing and proton motive force-dependent lactose transport. Six of 20 primary hits inhibited TonB-dependent activity in all tests. Comparison of their effects on [59Fe]Ent and [14C]lactose accumulation suggested several as proton ionophores, but two chemicals, ebselen and ST0082990, are likely not proton ionophores and may inhibit TonB-ExbBD. The facility of FLHTS against E. coli led us to adapt it to Acinetobacter baumannii We identified its FepA ortholog (AbaFepA), deleted and cloned its structural gene, genetically engineered 8 Cys substitutions in its surface loops, labeled them with fluorescein, and made fluorescence spectroscopic observations of FeEnt uptake in A. baumannii Several Cys substitutions in AbaFepA (S279C, T562C, and S665C) were readily fluoresceinated and then suitable as sensors of FeEnt transport. As in E. coli, the test monitored TonB-dependent FeEnt uptake by AbaFepA. In microtiter format with A. baumannii, FLHTS produced Z' factors 0.6 to 0.8. These data validated the FLHTS strategy against even distantly related Gram-negative bacterial pathogens. Overall, it discovered agents that block TonB-dependent transport and showed the potential to find compounds that act against Gram-negative CRE (carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae)/ESKAPE (Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter species) pathogens. Our results suggest that hundreds of such chemicals may exist in larger compound libraries.IMPORTANCE Antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria has spurred efforts to find novel compounds against new targets. The CRE/ESKAPE pathogens are resistant bacteria that include Acinetobacter baumannii, a common cause of ventilator-associated pneumonia and sepsis. We performed fluorescence high-throughput screening (FLHTS) against Escherichia coli to find inhibitors of TonB-dependent iron transport, tested them against A. baumannii, and then adapted the FLHTS technology to allow direct screening against A. baumannii This methodology is expandable to other drug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens. Compounds that block TonB action may interfere with iron acquisition from eukaryotic hosts and thereby constitute bacteriostatic antibiotics that prevent microbial colonization of human and animals. The FLHTS method may identify both species-specific and broad-spectrum agents against Gram-negative bacteria.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; ESKAPE pathogen; FepA; TonB; antibiotic resistance; ferric enterobactin; fluorescence assays; high throughput; iron transport.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High-Throughput Screening Assay for Inhibitors of TonB-Dependent Iron Transport.J Biomol Screen. 2016 Mar;21(3):316-22. doi: 10.1177/1087057115613788. Epub 2015 Oct 30. J Biomol Screen. 2016. PMID: 26518031
-
Siderophore-mediated iron acquisition by Klebsiella pneumoniae.J Bacteriol. 2024 May 23;206(5):e0002424. doi: 10.1128/jb.00024-24. Epub 2024 Apr 9. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38591913 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent sensors of siderophores produced by bacterial pathogens.J Biol Chem. 2022 Mar;298(3):101651. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101651. Epub 2022 Jan 29. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35101443 Free PMC article.
-
Three paradoxes of ferric enterobactin uptake.Front Biosci. 2003 Sep 1;8:s1422-36. doi: 10.2741/1233. Front Biosci. 2003. PMID: 12957833 Review.
-
Iron acquisition functions expressed by the human pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii.Biometals. 2009 Feb;22(1):23-32. doi: 10.1007/s10534-008-9202-3. Epub 2009 Jan 7. Biometals. 2009. PMID: 19130255 Review.
Cited by
-
Contribution of Active Iron Uptake to Acinetobacter baumannii Pathogenicity.Infect Immun. 2019 Mar 25;87(4):e00755-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00755-18. Print 2019 Apr. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 30718286 Free PMC article.
-
Universal fluorescent sensors of high-affinity iron transport, applied to ESKAPE pathogens.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 22;294(12):4682-4692. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006921. Epub 2019 Jan 24. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30679312 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Repurposing for the Treatment of Bacterial and Fungal Infections.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jan 28;10:41. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00041. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30745898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides from Plants: A cDNA-Library Based Isolation, Purification, Characterization Approach and Elucidating Their Modes of Action.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 13;22(16):8712. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168712. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Six tonB Gene Homologs in Bacteroides fragilis Revealed That tonB3 is Essential for Survival in Experimental Intestinal Colonization and Intra-Abdominal Infection.Infect Immun. 2022 Jan 25;90(1):e0046921. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00469-21. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Infect Immun. 2022. PMID: 34662212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weinberg ED. 1975. Nutritional immunity. Host's attempt to withold iron from microbial invaders; JAMA 231:39–41. - PubMed
-
- Harris WR, Carrano CJ, Raymond KN. 1979. Spectrophotometric determination of the proton-dependent stability constant of ferric enterobactin. J Am Chem Soc 101:2213–2214. doi:10.1021/ja00502a053. - DOI
-
- Carrano CJ, Raymond KN. 1979. Ferric ion sequestering agents. 2. Kinetics and mechanism of iron removal from transferrin by enterobactin and synthetic tricatechols. J Am Chem Soc 101:5401–5404.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

