Alpha-1 antitrypsin Pi*Z gene frequency and Pi*ZZ genotype numbers worldwide: an update
- PMID: 28243076
- PMCID: PMC5315200
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S125389
Alpha-1 antitrypsin Pi*Z gene frequency and Pi*ZZ genotype numbers worldwide: an update
Abstract
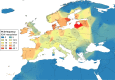
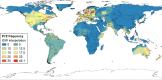
In alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), the Z allele is present in 98% of cases with severe disease, and knowledge of the frequency of this allele is essential from a public health perspective. However, there is a remarkable lack of epidemiological data on AATD worldwide, and many of the data currently used are outdated. Therefore, the objective of this study was to update the knowledge of the frequency of the Z allele to achieve accurate estimates of the prevalence and number of Pi*ZZ genotypes worldwide based on studies performed according to the following criteria: 1) samples representative of the general population, 2) AAT phenotyping characterized by adequate methods, and 3) measurements performed using a coefficient of variation calculated from the sample size and 95% confidence intervals. Studies fulfilling these criteria were used to develop maps with an inverse distance weighted (IDW)-interpolation method, providing numerical and graphical information of Pi*Z distribution worldwide. A total of 224 cohorts from 65 countries were included in the study. With the data provided by these cohorts, a total of 253,404 Pi*ZZ were estimated worldwide: 119,594 in Europe, 91,490 in America and Caribbean, 3,824 in Africa, 32,154 in Asia, 4,126 in Australia, and 2,216 in New Zealand. In addition, the IDW-interpolation maps predicted Pi*Z frequencies throughout the world even in some areas that lack real data. In conclusion, the inclusion of new well-designed studies and the exclusion of the low-quality ones have significantly improved the reliability of results, which may be useful to plan strategies for future research and diagnosis and to rationalize the therapeutic resources available.
Keywords: SERPINA1; alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency; genetic epidemiology; geographic information system; inverse distance weighted interpolation; protease inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- De Serres F, Blanco I. Role of alpha-1 antitrypsin in human health and disease. J Intern Med. 2014;276(4):311–335. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Statement Standards for the diagnosis and management of individuals with alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;168:818–900. - PubMed
-
- Casas F, Blanco I, Martínez MT, et al. Indications for active case searches and intravenous alpha-1 antitrypsin treatment for patients with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency chronic pulmonary obstructive disease: an update. Arch Bronconeumol. 2015;51(4):185–192. - PubMed
-
- Stone H, Pye A, Stockley RA. Disease associations in alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. Respir Med. 2014;108(2):338–343. - PubMed
-
- Lee JH, Brantly M. Molecular mechanisms of alpha1-antitrypsin null alleles. Respir Med. 2000;94(Suppl C):S7–S11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

