Production of Isolated Giant Unilamellar Vesicles under High Salt Concentrations
- PMID: 28243205
- PMCID: PMC5303729
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00063
Production of Isolated Giant Unilamellar Vesicles under High Salt Concentrations
Abstract
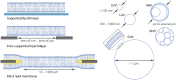
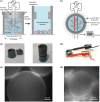
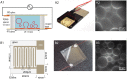
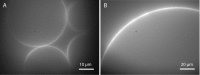
The cell membrane forms a dynamic and complex barrier between the living cell and its environment. However, its in vivo studies are difficult because it consists of a high variety of lipids and proteins and is continuously reorganized by the cell. Therefore, membrane model systems with precisely controlled composition are used to investigate fundamental interactions of membrane components under well-defined conditions. Giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) offer a powerful model system for the cell membrane, but many previous studies have been performed in unphysiologically low ionic strength solutions which might lead to altered membrane properties, protein stability and lipid-protein interaction. In the present work, we give an overview of the existing methods for GUV production and present our efforts on forming single, free floating vesicles up to several tens of μm in diameter and at high yield in various buffer solutions with physiological ionic strength and pH.
Keywords: double emulsion; electroformation; giant unilamellar vesicle; lipid membrane; microfluidic jetting; micropipette aspiration; model membrane system; swelling.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Giant unilamellar vesicle electroformation from lipid mixtures to native membranes under physiological conditions.Methods Enzymol. 2009;465:161-76. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(09)65009-6. Methods Enzymol. 2009. PMID: 19913167
-
Electroformation of Giant Unilamellar Vesicles from Damp Films in Conditions Involving High Cholesterol Contents, Charged Lipids, and Saline Solutions.Membranes (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;14(10):215. doi: 10.3390/membranes14100215. Membranes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452827 Free PMC article.
-
Electroformation of giant unilamellar vesicles from native membranes and organic lipid mixtures for the study of lipid domains under physiological ionic-strength conditions.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;606:105-14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-447-0_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20013393
-
Giant unilamellar vesicles - a perfect tool to visualize phase separation and lipid rafts in model systems.Acta Biochim Pol. 2009;56(1):33-9. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Acta Biochim Pol. 2009. PMID: 19287805 Review.
-
Self-Assembly of Giant Unilamellar Vesicles by Film Hydration Methodologies.Adv Biosyst. 2019 Jun;3(6):e1800324. doi: 10.1002/adbi.201800324. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Adv Biosyst. 2019. PMID: 32648708 Review.
Cited by
-
Microfluidics-mediated Liposomal Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: Recent Developments on Advanced Devices and Technologies.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(14):1185-1211. doi: 10.2174/0115680266286460240220073334. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38424436 Review.
-
Vesicle-based artificial cells: materials, construction methods and applications.Mater Horiz. 2022 Mar 7;9(3):892-907. doi: 10.1039/d1mh01431e. Mater Horiz. 2022. PMID: 34908080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
USE OF ARTIFICIAL CELLS AS DRUG CARRIERS.Mater Chem Front. 2021 Sep 21;5(18):6672-6692. doi: 10.1039/d1qm00717c. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Mater Chem Front. 2021. PMID: 38344270 Free PMC article.
-
A general computational framework for the dynamics of single- and multi-phase vesicles and membranes.J Comput Phys. 2022 Feb 1;450:110815. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2021.110815. Epub 2021 Nov 8. J Comput Phys. 2022. PMID: 35355617 Free PMC article.
-
Glycan-decorated protocells: novel features for rebuilding cellular processes.Interface Focus. 2019 Apr 6;9(2):20180084. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2018.0084. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Interface Focus. 2019. PMID: 30842879 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abkarian M., Loiseau E., Massiera G. (2011). Continuous droplet interface crossing encapsulation (cDICE) for high throughput monodisperse vesicle design. Soft Matt. 7, 4610–4614. 10.1039/c1sm05239j - DOI
-
- Angelova M. I., Dimitrov D. S. (1986). Liposome electroformation. Faraday Discuss. Chem. Soc. 81:303 10.1039/dc9868100303 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

