Preventive Gabapentin versus Pregabalin to Decrease Postoperative Pain after Lumbar Microdiscectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 28243376
- PMCID: PMC5326739
- DOI: 10.4184/asj.2017.11.1.93
Preventive Gabapentin versus Pregabalin to Decrease Postoperative Pain after Lumbar Microdiscectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Study design: Randomized controlled trial.
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to compare pregabalin and gabapentin for mean postoperative visual analog score (VAS) for pain in patients undergoing single-level lumbar microdiscectomy for intervertebral disc prolapse at a tertiary care hospital.
Overview of literature: Pregabalin has a superior pharmacokinetic profile and analgesic effect at lower doses than gabapentin; however, analgesic efficacy must be established during the perioperative period after lumbar spine surgery.
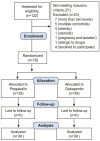
Methods: This randomized controlled trial was carried out at our institute from February to October 2011 on 78 patients, with 39 participants in each study group. Patients undergoing lumbar microdiscectomy were randomized to group A (gabapentin) or group B (pregabalin) and started on trial medicines one week before surgery. The VAS for pain was recorded at 24 hours and one week postoperatively.
Results: Both groups had similar baseline variables, with mean ages of 42 and 39 years in groups A and B, respectively, and a majority of male patients in each group. The mean VAS values for pain at 24 hours for gabapentin vs. pregabalin were comparable (1.97±0.84 vs. 1.6±0.87, respectively; p=0.087) as were the results at one week after surgery (0.27±0.45 vs. 0.3±0.46, respectively; p=0.79). None of the patients required additional analgesia postoperatively. After adjusting for age and sex, the VAS value for group B patients was 0.028 points lower than for group A patients, but this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.817, R2=0.018).
Conclusions: Pregabalin is equivalent to gabapentin for the relief of postoperative pain at a lower dose in patients undergoing lumbar microdiscectomy. Therefore, other factors, such as dose, frequency, cost, pharmacokinetics, and side effects of these medicines, should be taken into account whenever it is prescribed.
Keywords: Gabapentin; Intervertebral disc displacement; Lumbar vertebrae; Postoperative pain; Pregabalin.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Similar articles
-
Role of Pregabalin to Decrease Postoperative Pain in Microdiscectomy: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Cureus. 2021 Jan 22;13(1):e12870. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12870. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33633899 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Efficacy of Pregabalin and Gabapentin for Preemptive Analgesia in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Patients: A Randomised Double-Blind Study.Cureus. 2023 Oct 9;15(10):e46719. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46719. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021908 Free PMC article.
-
Gabapentin versus pregabalin in relieving early post-surgical neuropathic pain in patients after lumbar disc herniation surgery: a prospective clinical trial.Neurol Res. 2014 Dec;36(12):1080-5. doi: 10.1179/1743132814Y.0000000404. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Neurol Res. 2014. PMID: 24938318 Clinical Trial.
-
The Efficacy of Preoperative Gabapentin in Spinal Surgery: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Pain Physician. 2017 Nov;20(7):649-661. Pain Physician. 2017. PMID: 29149144 Review.
-
Perioperative gabapentin and post cesarean pain control: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2019 Feb;233:98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2018.11.026. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2019. PMID: 30583095
Cited by
-
Pregabalin as an effective treatment for acute postoperative pain following spinal surgery without major side effects: protocol for a prospective, randomized controlled, double-blinded trial.Trials. 2023 Jun 22;24(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07438-2. Trials. 2023. PMID: 37349841 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the effectiveness of pregabalin and gabapentin in patients with lumbar radiculopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pain Pract. 2024 Oct 11;25(1):e13424. doi: 10.1111/papr.13424. Online ahead of print. Pain Pract. 2024. PMID: 39394725 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Pregabalin to Decrease Postoperative Pain in Microdiscectomy: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Cureus. 2021 Jan 22;13(1):e12870. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12870. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33633899 Free PMC article.
-
Unfolding the Truth; the Way Towards Painfree Spine Surgery.Asian J Neurosurg. 2018 Oct-Dec;13(4):1303-1304. doi: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_68_17. Asian J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30459924 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Different Gabapentin and Pregabalin Dosages for Perioperative Pain Control in Patients Undergoing Spine Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Aug 1;6(8):e2328121. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.28121. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37556139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blumenthal S, Borgeat A, Nadig M, Min K. Postoperative analgesia after anterior correction of thoracic scoliosis: a prospective randomized study comparing continuous double epidural catheter technique with intravenous morphine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31:1646–1651. - PubMed
-
- Feldstein G, Ramanathan S. Obstetrical lumbar epidural anesthesia in patients with previous posterior spinal fusion for kyphoscoliosis. Anesth Analg. 1985;64:83–85. - PubMed
-
- Fisher CG, Belanger L, Gofton EG, et al. Prospective randomized clinical trial comparing patient-controlled intravenous analgesia with patient-controlled epidural analgesia after lumbar spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2003;28:739–743. - PubMed
-
- Kehlet H. Multimodal approach to control postoperative pathophysiology and rehabilitation. Br J Anaesth. 1997;78:606–617. - PubMed
-
- Perkins FM, Kehlet H. Chronic pain as an outcome of surgery: a review of predictive factors. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:1123–1133. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials