Microfluidic setup for on-line SERS monitoring using laser induced nanoparticle spots as SERS active substrate
- PMID: 28243562
- PMCID: PMC5301917
- DOI: 10.3762/bjnano.8.26
Microfluidic setup for on-line SERS monitoring using laser induced nanoparticle spots as SERS active substrate
Abstract
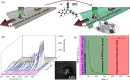
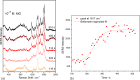
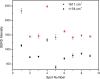
A microfluidic setup which enables on-line monitoring of residues of malachite green (MG) using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) is reported. The SERS active substrate was prepared via laser induced synthesis of silver or gold nanoparticles spot on the bottom of a 200 μm inner dimension glass capillary, by focusing the laser beam during a continuous flow of a mixture of silver nitrate or gold chloride and sodium citrate. The described microfluidic setup enables within a few minutes the monitoring of several processes: the synthesis of the SERS active spot, MG adsorption to the metal surface, detection of the analyte when saturation of the SERS signal is reached, and finally, the desorption of MG from the spot. Moreover, after MG complete desorption, the regeneration of the SERS active spot was achieved. The detection of MG was possible down to 10-7 M concentration with a good reproducibility when using silver or gold spots as SERS substrate.
Keywords: SERS; gold nanoparticles; malachite green; microfluidic setup; silver nanoparticles.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In situ laser-induced photochemical silver substrate synthesis and sequential SERS detection in a flow cell.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011 May;400(3):815-20. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-4798-5. Epub 2011 Feb 26. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21359570
-
On-column silver substrate synthesis and surface-enhanced Raman detection in capillary electrophoresis.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Mar;396(6):2341-8. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-3468-3. Epub 2010 Feb 3. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20127318
-
Self-Concentrated Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering-Active Droplet Sensor with Three-Dimensional Hot Spots for Highly Sensitive Molecular Detection in Complex Liquid Environments.ACS Sens. 2020 Nov 25;5(11):3420-3431. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.0c01276. Epub 2020 Sep 29. ACS Sens. 2020. PMID: 32929960
-
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering: realization of localized surface plasmon resonance using unique substrates and methods.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009 Aug;394(7):1747-60. doi: 10.1007/s00216-009-2762-4. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009. PMID: 19384546 Review.
-
Surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) with biopolymer encapsulated silver nanosubstrates for rapid detection of foodborne pathogens.Int J Food Microbiol. 2013 Oct 1;167(1):67-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.05.013. Epub 2013 May 22. Int J Food Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23806291 Review.
Cited by
-
Self-Organized SERS Substrates with Efficient Analyte Enrichment in the Hot Spots.ACS Omega. 2024 Jan 18;9(4):4819-4830. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08393. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38313516 Free PMC article.
-
SERS of nitro group compounds for sensing of explosives.RSC Adv. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):252-260. doi: 10.1039/d4ra07309f. eCollection 2025 Jan 2. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 39758932 Free PMC article.
-
Raman and Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Detection in Flowing Solutions for Complex Mixture Analysis.Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2024 Jul;17(1):411-432. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-061522-035207. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2024. PMID: 38382105 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jakšić O M, Randjelović D V, Jakšić Z S, Čupić T D, Kolar-Anić L Z. Chem Eng Res Des. 2014;92:91–101. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2013.06.033. - DOI
-
- Hidayah N, Abu Bakar F, Mahyudin N A, Faridah S, Nur-Azura M S, Zaman M Z. Int Food Res J. 2013;20:1511–1519.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
