Safety of Using Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitor in Experimental Glaucoma Filtration Surgery
- PMID: 28244295
- PMCID: PMC5334167
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.4.666
Safety of Using Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitor in Experimental Glaucoma Filtration Surgery
Abstract
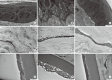
We evaluated the safety of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitor in experimental glaucoma filtration surgery in an animal model. Fifteen New Zealand white rabbits underwent an experimental trabeculectomy and were randomly allocated into 3 groups according to the adjuvant agent: no treatment group (n = 5), 0.02% mitomycin C (MMC) soaking group (n = 5), and MMP inhibitor (ilomastat) subconjunctival injection group (n = 5). Slit lamp examination with Seidel testing, pachymetry, and specular microscopy was performed preoperatively and postoperatively. The conjunctiva and ciliary body toxicity were evaluated with scores according to the pathologic grading systems. Electron microscopy was used to examine the structural changes in cornea, conjunctiva, and ciliary body. In the ilomastat-treated group, there was no statistically significant change in central corneal thickness preoperatively and at 28 days postoperatively (P = 0.655). There were also no significant changes in specular microscopy findings over the duration of the study in the ilomastat-treated group. The conjunctival toxicity score was 1 in the control group, 1.5 in the ilomastat-treated group, and 2 in the MMC-treated group. When assessing ciliary body toxicity scores, the ilomastat-treated group score was 0.5 and the MMC-treated group score was 1.5. Transmission electron microscopy did not show structural changes in the cornea and ciliary body whereas the structural changes were noticed in MMC group. A single subconjunctival injection of MMP inhibitor during the experimental trabeculectomy showed a less toxic affect in the rabbit cornea, conjunctiva, and ciliary body compared to MMC.
Keywords: Filtration; Glaucoma; Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitor.
© 2017 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prolonged antiscarring effects of ilomastat and MMC after experimental glaucoma filtration surgery.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Jun;46(6):2018-22. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0820. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15914618
-
Sequential Therapy with Saratin, Bevacizumab and Ilomastat to Prolong Bleb Function following Glaucoma Filtration Surgery in a Rabbit Model.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 22;10(9):e0138054. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138054. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26394037 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of mitomycin C on ciliary body and intraocular pressure with various application depths: an experimental study.Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005 Apr;33(2):169-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-9071.2005.00989.x. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005. PMID: 15807826
-
Paclitaxel Associated With Lipid Nanoparticles as a New Antiscarring Agent in Experimental Glaucoma Surgery.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Mar;57(3):971-8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-18671. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 26962693
-
The toxicology of mitomycin C on the ciliary body.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1996 Apr;7(2):72-9. doi: 10.1097/00055735-199604000-00013. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1996. PMID: 10163326 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition in cultured human Tenon's capsule fibroblasts.BMC Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 29;25(1):434. doi: 10.1186/s12886-025-04258-7. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40730956 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Therapies for the Prevention of Fibrosis in Glaucoma Filtration Surgery.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 21;11(3):657. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030657. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrix Metalloproteinases and Glaucoma.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 25;12(10):1368. doi: 10.3390/biom12101368. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291577 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allingham RR, Damji KF, Freedman S, Moroi SE, Shafranov G, Shields MB, editors. Shields' Textbook of Glaucoma. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Willliams & Wilkins; 2005. Filtering surgery; pp. 568–609.
-
- Jampel HD. Effect of brief exposure to mitomycin C on viability and proliferation of cultured human Tenon’s capsule fibroblasts. Ophthalmology. 1992;99:1471–1476. - PubMed
-
- Smith S, D’Amore PA, Dreyer EB. Comparative toxicity of mitomycin C and 5-fluorouracil in vitro. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994;118:332–337. - PubMed
-
- Nuyts RM, Felten PC, Pels E, Langerhorst CT, Geijssen HC, Grossniklaus HE, Greve EL. Histopathologic effects of mitomycin C after trabeculectomy in human glaucomatous eyes with persistent hypotony. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994;118:225–237. - PubMed
-
- Hau S, Barton K. Corneal complications of glaucoma surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2009;20:131–136. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

