Ischemic Optic Neuropathy in Cardiac Surgery: Incidence and Risk Factors in the United States from the National Inpatient Sample 1998 to 2013
- PMID: 28244936
- PMCID: PMC5395417
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001533
Ischemic Optic Neuropathy in Cardiac Surgery: Incidence and Risk Factors in the United States from the National Inpatient Sample 1998 to 2013
Abstract
Background: Ischemic optic neuropathy is the most common form of perioperative visual loss, with highest incidence in cardiac and spinal fusion surgery. To date, potential risk factors have been identified in cardiac surgery by only small, single-institution studies. To determine the preoperative risk factors for ischemic optic neuropathy, the authors used the National Inpatient Sample, a database of inpatient discharges for nonfederal hospitals in the United States.
Methods: Adults aged 18 yr or older admitted for coronary artery bypass grafting, heart valve repair or replacement surgery, or left ventricular assist device insertion in National Inpatient Sample from 1998 to 2013 were included. Risk of ischemic optic neuropathy was evaluated by multivariable logistic regression.
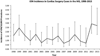
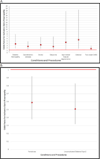
Results: A total of 5,559,395 discharges met inclusion criteria with 794 (0.014%) cases of ischemic optic neuropathy. The average yearly incidence was 1.43 of 10,000 cardiac procedures, with no change during the study period (P = 0.57). Conditions increasing risk were carotid artery stenosis (odds ratio, 2.70), stroke (odds ratio, 3.43), diabetic retinopathy (odds ratio, 3.83), hypertensive retinopathy (odds ratio, 30.09), macular degeneration (odds ratio, 4.50), glaucoma (odds ratio, 2.68), and cataract (odds ratio, 5.62). Female sex (odds ratio, 0.59) and uncomplicated diabetes mellitus type 2 (odds ratio, 0.51) decreased risk.
Conclusions: The incidence of ischemic optic neuropathy in cardiac surgery did not change during the study period. Development of ischemic optic neuropathy after cardiac surgery is associated with carotid artery stenosis, stroke, and degenerative eye conditions.
Figures

References
-
- Shapira OM, Kimmel WA, Lindsey PS, Shahian DM. Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy after open heart operations. Ann Thorac Surg. 1996;61:660–666. - PubMed
-
- Nuttall GA, Garrity JA, Dearani JA, Abel MD, Schroeder DR, Mullany CJ. Risk factors for ischemic optic neuropathy after cardiopulmonary bypass: a matched case/control study. Anesth Analg. 2001;93:1410–1416. table of contents. - PubMed
-
- Shen Y, Drum M, Roth S. The prevalence of perioperative visual loss in the United States: a 10-year study from 1996 to 2005 of spinal, orthopedic, cardiac, and general surgery. Anesth Analg. 2009;109:1534–1545. - PubMed
-
- Kalyani SD, Miller NR, Dong LM, Baumgartner WA, Alejo DE, Gilbert TB. Incidence of and risk factors for perioperative optic neuropathy after cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004;78:34–37. - PubMed
-
- Postoperative Visual Loss Study G. Risk factors associated with ischemic optic neuropathy after spinal fusion surgery. Anesthesiology. 2012;116:15–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

