Eplerenone for hypertension
- PMID: 28245343
- PMCID: PMC6464701
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008996.pub2
Eplerenone for hypertension
Abstract
Background: Eplerenone is an aldosterone receptor blocker that is chemically derived from spironolactone. In Canada, it is indicated for use as adjunctive therapy to reduce mortality for heart failure patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II systolic chronic heart failure and left ventricular systolic dysfunction. It is also used as adjunctive therapy for patients with heart failure following myocardial infarction. Additionally, it is indicated for the treatment of mild and moderate essential hypertension for patients who cannot be treated adequately with other agents. It is important to determine the clinical impact of all antihypertensive medications, including aldosterone antagonists, to support their continued use in essential hypertension. No previous systematic reviews have evaluated the effect of eplerenone on cardiovascular morbidity, mortality, and magnitude of blood pressure lowering in patients with hypertension.
Objectives: To assess the effects of eplerenone monotherapy versus placebo for primary hypertension in adults. Outcomes of interest were all-cause mortality, cardiovascular events (fatal or non-fatal myocardial infarction), cerebrovascular events (fatal or non fatal strokes), adverse events or withdrawals due to adverse events, and systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Hypertension Specialised Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, and two trials registers up to 3 March 2016. We handsearched references from retrieved studies to identify any studies missed in the initial search. We also searched for unpublished data by contacting the corresponding authors of the included studies and pharmaceutical companies involved in conducting studies on eplerenone monotherapy in primary hypertension. The search had no language restrictions.
Selection criteria: We selected randomized placebo-controlled trials studying adult patients with primary hypertension. We excluded studies in people with secondary or gestational hypertension and studies where participants were receiving multiple antihypertensives.
Data collection and analysis: Three review authors independently reviewed the search results for studies meeting our criteria. Three review authors independently extracted data and assessed trial quality using a standardized data extraction form. A fourth independent review author resolved discrepancies or disagreements. We performed data extraction and synthesis using a standardized format on Covidence. We conducted data analysis using Review Manager 5.
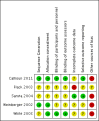
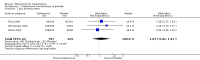
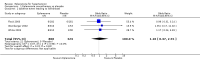
Main results: A total of 1437 adult patients participated in the five randomized parallel group studies, with treatment durations ranging from 8 to 16 weeks. The daily doses of eplerenone ranged from 25 mg to 400 mg daily. Meta-analysis of these studies showed a reduction in systolic blood pressure of 9.21 mmHg (95% CI -11.08 to -7.34; I2 = 58%) and a reduction of diastolic pressure of 4.18 mmHg (95% CI -5.03 to -3.33; I2 = 0%) (moderate quality evidence).There may be a dose response effect for eplerenone in the reduction in systolic blood pressure at doses of 400 mg/day. However, this finding is uncertain, as it is based on a single included study with low quality evidence. Overall there does not appear to be a clinically important dose response in lowering systolic or diastolic blood pressure at eplerenone doses of 50 mg to 400 mg daily. There did not appear to be any differences in the number of patients who withdrew due to adverse events or the number of patients with at least one adverse event in the eplerenone group compared to placebo. However, only three of the five included studies reported adverse events. Most of the included studies were of moderate quality, as we judged multiple domains as being at unclear risk in the 'Risk of bias' assessment.
Authors' conclusions: Eplerenone 50 to 200 mg/day lowers blood pressure in people with primary hypertension by 9.21 mmHg systolic and 4.18 mmHg diastolic compared to placebo, with no difference of effect between doses of 50 mg/day to 200 mg/day. A dose of 25 mg/day did not produce a statistically significant reduction in systolic or diastolic blood pressure and there is insufficient evidence for doses above 200 mg/day. There is currently no available evidence to determine the effect of eplerenone on clinically meaningful outcomes such as mortality or morbidity in hypertensive patients. The evidence available on side effects is insufficient and of low quality, which makes it impossible to draw conclusions about potential harm associated with eplerenone treatment in hypertensive patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Sarah C Masson: none known.
Aaron M Tejani: none known.
Sarah N Stabler: none known.
Matthew P Tsang: none known.
Anthony Tung: none known.
Angus TV Kinkade: none known.
Tina SC Tam: none known.
May HY Wu: none known.
Figures









Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008996
References
References to studies included in this review
Calhoun 2011 {published data only}
-
- Calhoun DA, White WB, Krum H, Guo W, Bermann G, Trapani A, et al. Effects of a novel aldosterone synthase inhibitor for treatment of primary hypertension: results of a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐ and active‐controlled phase 2 trial. Circulation 2011;124(18):1945‐55. [DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.029892] - DOI - PubMed
Flack 2003 {published data only}
Saruta 2004 {published data only}
-
- Saruta T, Kageyama S, Ogihara T, Hiwada K, Ogawa M, Tawara K, et al. Efficacy and safety of the selective aldosterone blocker eplerenone in Japanese patients with hypertension: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, dose‐ranging study. Journal of Clinical Hypertension (Greenwich) 2004;6(4):175‐83; quiz 184‐5. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2004.03146.x] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Weinberger 2002 {published data only}
-
- Weinberger MH, Roniker B, Krause SL, Weiss RJ. Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, in mild‐to‐moderate hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 2002;15(8):709‐16. [PUBMED: 12160194] - PubMed
White 2003 {published data only}
-
- White WB, Carr AA, Krause S, Jordan R, Roniker B, Oigman W. Assessment of the novel selective aldosterone blocker eplerenone using ambulatory and clinical blood pressure in patients with systemic hypertension. American Journal of Cardiology 2003;92(1):38‐42. [DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9149(03)00461-2] - DOI - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Amar 2013 {published data only}
Ando 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ando K, Ohtsu H, Arakawa Y, Kubota K, Yamaguchi T, Nagase M, EVALUATE investigators. Rationale and design of the Eplerenone combination Versus conventional Agents to Lower blood pressure on Urinary Antialbuminuric Treatment Effect (EVALUATE) trial: a double‐blinded randomized placebo‐controlled trial to evaluate the antialbuminuric effects of an aldosterone blocker in hypertensive patients with albuminuria. Hypertension Research 2010;33(6):616‐21. [DOI: 10.1038/hr.2010.46] - DOI - PubMed
Ando 2014a {published data only}
-
- Ando K, Ohtsu H, Uchida S, Kaname S, Arakawa Y, Fujita T, EVALUATE Study Group. Anti‐albuminuric effect of the aldosterone blocker eplerenone in non‐diabetic hypertensive patients with albuminuria: a double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2014;2(12):944‐53. [DOI: 10.1016/s2213-8587(14)70194-9] - DOI - PubMed
Ando 2014b {published data only}
-
- Ando K, Ohtsu H, Uchida S, Kaname S, Arakawa Y, Fujita T, EVALUATE Study Group. Correction to Antialbuminuric effect of the aldosterone blocker eplerenone in non‐diabetic hypertensive patients with albuminuria: a double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled trial [Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2, (2014) 944‐953]. Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2015;3(4):e3. [DOI: 10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00055-8] - DOI - PubMed
Basile 2009 {published data only}
Blanchard 2015 {published data only}
Burger 2005 {published data only}
Burgess 2003 {published data only}
-
- Burgess ED, Lacourciere Y, Ruilope‐Urioste LM, Oparil S, Kleiman JH, Krause S, et al. Long‐term safety and efficacy of the selective aldosterone blocker eplerenone in patients with essential hypertension. Clinical Therapy 2003;25(9):2388‐404. - PubMed
Calhoun 2008 {published data only}
CCOHTA 2003 {published data only}
-
- The Canadian Coordinating Office for Health Technology Assessment (CCOHTA). Eplerenone for the treatment of hypertension. Emerging Drug List 2003; Vol. 37:1‐3.
Chaturvedi 2014 {published data only}
Christou 2011 {published data only}
-
- Christou DD, Hwang MH, Yoo JK, Luttrell MJ, Cernosek MM, Meade TH, et al. Effect of acute mineralocorticoid receptor blockade on flow‐mediated dilation in middle aged and older adults with metabolic syndrome. Journal of Diabetes 2011;3:239‐40. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1753-0407.2011.00122.x] - DOI
Christou 2012 {published data only}
-
- Christou DD, Yoo JK, Hwang MH, Luttrell M, Kim HK, Meade TH, et al. Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade does not result in arterial destiffening in healthy older adults. Hypertension 2012;60(Suppl 1):A13.
Cleland 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cleland JGF, Coletta AP, Clark AL. Clinical trials update from the American College of Cardiology 2007: ALPHA, EVEREST, FUSION II, VALIDD, PARR‐2, REMODEL, SPICE, COURAGE, COACH, REMADHE, pro‐BNP for the evaluation of dyspnoea and THIS‐diet. European Journal of Heart Failure 2007;9(6‐7):740‐5. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2007.04.004] - DOI - PubMed
Collier 2013 {published data only}
-
- Collier TJ, Pocock SJ, McMurray JJV, Zannad F, Krum H, Veldhuisen DJ, et al. The impact of eplerenone at different levels of risk in patients with systolic heart failure and mild symptoms: insight from a novel risk score for prognosis derived from the EMPHASIS‐HF trial. European Heart Journal 2013;34(36):2823‐9. [DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht247] - DOI - PubMed
Conti 2003 {published data only}
Dahal 2015 {published data only}
Davis 2003 {published data only}
-
- Davis KL, Nappi JM. The cardiovascular effects of eplerenone, a selective aldosterone‐receptor antagonist. Clinical Therapeutics 2003;25(11):2647‐68. - PubMed
Derer 2010 {published data only}
-
- Derer W, Dechend R, Muller DN. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: inhibition of the renin angiotensin system [Welchen Stellenwert haben sie in der antihypertensien Therapie?]. MMW Fortschritte der Medizin 2010;152(6):48‐9. - PubMed
Deswal 2010 {published data only}
Deswal 2011 {published data only}
Dieterich 2005 {published data only}
-
- Dieterich HA, Wendt C, Saborowski F. Cardioprotection by aldosterone receptor antagonism in heart failure. Part I. The role of aldosterone in heart failure. Fiziol Cheloveka 2005;31(6):97‐105. - PubMed
Dobrucki 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dobrucki T, Januszewicz A, Sitkiewicz D, Januszewicz W. A New Face of Aldosterone [Aldosteron ‐ Hormon o nowym obliczu]. Nadcisnienie Tetnicze 2003;7(4):271‐9.
Epstein 1998 {published data only}
-
- Epstein M, Alexander JC, Roniker B. Eplerenone, a new selective aldosterone receptor antagonist (SARA): efficacy in patients with mild to moderate hypertension [Abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1998;9(Program & Abstracts):322A‐3A.
Epstein 2002 {published data only}
-
- Epstein M, Buckalew V, Martinez F. Antiproteinuric efficacy of eplerenone, enalapril, and eplerenone/enalapril combination therapy in diabetic hypertensives with microalbuminuria [Abstract no: OR54]. American Journal of Hypertension 2002;15(4 Suppl 1):24A.
Eschalier 2013 {published data only}
-
- Eschalier R, McMurray JJ, Swedberg K, Veldhuisen DJ, Krum H, Pocock SJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of eplerenone in patients at high risk for hyperkalemia and/or worsening renal function: analyses of the EMPHASIS‐HF study subgroups (Eplerenone in Mild Patients Hospitalization And SurvIval Study in Heart Failure). Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2013;62:1585‐93. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.04.086] - DOI - PubMed
Flammer 2013 {published data only}
-
- Flammer A, Sudano I, Enseleit F, Luscher TF, Noll G Ruschitzka F. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism in patients with coronary artery disease and preserved ejection fraction‐a randomized, double‐blind trial. European Journal of Heart Failure 2013;12:S222‐S223. [DOI: 10.1093/eurjhf/hst009] - DOI
Funder 2005 {published data only}
-
- Funder JW. ACE inhibitors and mineralocorticoid receptor blockade in patients with congestive heart failure. Current Diabetes Reports 2005;5(1):36‐40. - PubMed
Funder 2010 {published data only}
Hameedi 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hameedi A, Chadow HL. The promise of selective aldosterone receptor antagonists for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure. Current Hypertension Reports 2000;2(4):378‐83. - PubMed
Hollenberg 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hollenberg NK, Williams GH Anderson R, Akhras KS, Bittman RM, Krause SL. Symptoms and the distress they cause: comparison of an aldosterone antagonist and a calcium channel blocking agent in patients with systolic hypertension. Archives of Internal Medicine 2003;163(13):1543‐8. - PubMed
Hollenberg 2004 {published data only}
Hwang 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hwang MH, Yoo JK, Luttrell MJ, Cernosek MM, Meade TH, English MW, et al. Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade does not improve vascular endothelial function in older adults with metabolic syndrome [Abstract]. FASEB Journal 2011;25:Abstract no: 821.45.
Hwang 2013 {published data only}
Jansen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Jansen PM, Boomsma F, Meiracker AH, Dutch ARRAT investigators. Aldosterone‐to‐renin ratio as a screening test for primary aldosteronism‐‐the Dutch ARRAT Study. Netherlands Journal of Medicine 2008;66(5):220‐8. - PubMed
Joffe 2007 {published data only}
-
- Joffe HV, Kwong RY, Gerhard‐Herman MD, Rice C, Feldman K, Adler GK. Beneficial effects of eplerenone versus hydrochlorothiazide on coronary circulatory function in patients with diabetes mellitus. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2007;92(7):2552‐8. [DOI: 10.1210/jc.2007-0393] - DOI - PubMed
Karagiannis 2009 {published data only}
Karns 2013 {published data only}
Krum 2002 {published data only}
-
- Krum H, Nolly H, Workman D, He W, Roniker B, Krause S, et al. Efficacy of eplerenone added to renin‐angiotensin blockade in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 2002;40(2):117‐23. - PubMed
Levy 2004 {published data only}
-
- Levy DG, Rocha R, Funder JW. Distinguishing the antihypertensive and electrolyte effects of eplerenone. Journal of Clinical and Endocrinology Metabolism 2004;89(6):2736‐40. - PubMed
Li 2010 {published data only}
-
- Li, JS, Flynn JT, Portman R, Davis I, Ogawa M, Shi H, Pressler ML. The efficacy and safety of the novel aldosterone antagonist eplerenone in children with hypertension: a randomized, double‐blind, dose‐response study. Journal of Pediatrics 2010;157(2):282‐7. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.02.042] - DOI - PubMed
Magill 2003 {published data only}
-
- Magill MK, Gunning K, Saffel‐Shrier S, Gay C. New developments in the management of hypertension. American Family Physician 2003;68(5):853‐8. - PubMed
Magni 2005 {published data only}
-
- Magni P, Motta M. Aldosterone receptor antagonists: biology and novel therapeutic applications. Current Hypertension Reports 2005;7(3):206‐11. - PubMed
Mantero 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mantero F, Lucarelli G. Aldosterone antagonists in hypertension and heart failure. Annales d'endocrinologie 2000;61(1):52‐60. - PubMed
Montalescot 2014 {published data only}
-
- Montalescot G, Pitt B, Lopez De Sa E, Hamm CW, Flather M, Verheugt F, et al. Early eplerenone treatment in patients with acute ST‐elevation myocardial infarction without heart failure: the Randomized Double‐Blind Reminder Study. European Heart Journal 2014;35:2295‐302. [DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu164] - DOI - PubMed
NCT00147589 {published data only}
-
- Pfizer. Peds I (Pediatric Eplerenone Development Study I): a randomized, double‐blind, placebo withdrawal, parallel group, dose‐response study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of eplerenone In the treatment of hypertension in children. ClinicalTrials.gov 2008. [NCT00147589]
NCT00147615 {published data only}
-
- Pfizer. Peds II (Pediatric Eplerenone Development Study II)‐‐An open label, long‐term study to evaluate the safety of eplerenone in the treatment of hypertension in children. ClinicalTrials.gov 2004. [NCT00147615]
NCT00649311 {published data only}
-
- Pfizer. A study to evaluate the efficacy of eplerenone compared with losartan for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate hypertension. ClinicalTrials.gov 2009. [NCT00649311]
NCT00758524 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. A multi‐center, randomized, double‐blind, placebo and active controlled, parallel group, dose finding study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of LCI699, a new experimental antihypertensive drug, in patients with essential hypertension. ClinicalTrials.gov 2012. [NCT00758524]
NCT00817635 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. A study to evaluate the effects of LCI699 on safety and efficacy in subjects with resistant hypertension receiving combination therapy with three or more antihypertensive drugs, including a diuretic. ClinicalTrials.gov 2012. [NCT00817635]
NCT00825188 {published data only}
-
- Wofford M, University of Mississippi Medical Center. A study of the effects of eplerenone and amlodipine on blood pressure and basal metabolic rate in obese hypertensives. ClinicalTrials.gov 2014. [NCT00825188]
NCT00980031 {published data only}
-
- Holmberg MJ, Creighton University. Aldosterone blockade to prevent myocardial remodeling in patients with controlled essential hypertension. ClinicalTrials.gov 2014. [NCT00980031]
NCT01275352 {published data only}
-
- Washington University School of Medicine. A randomized, double blind pilot study evaluating CLCNKA (Ka Renal Chloride Channel[ClC‐Ka]) polymorphism effects on hypertrophy regression in caucasian hypertensive patients treated with eplerenone. ClinicalTrials.gov 2015. [NCT01275352]
NCT01373086 {published data only}
-
- Novartis. LFF269 compared to placebo after treatment in subjects with essential hypertension. ClinicalTrials.gov 2012. [NCT01373086]
NCT02345044 {published data only}
-
- Daiichi Sankyo Inc. A study to evaluate efficacy and safety of CS‐3150 in Japanese hypertensive subjects. ClinicalTrials.gov 2016. [NCT02345044]
Pelliccia 2014 {published data only}
Pelliccia 2015 {published data only}
Pitt 2004 {published data only}
-
- Pitt B, Reichek N, Willenbrock R, et al. Trial suggests that combining eplerenone and enalapril reduces left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertension more effectively than either treatment alone. Evidence‐based Cardiovascular Medicine 2004;8(1):16‐7; discussion 18‐9, 20‐1. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ebcm.2003.12.012] - DOI - PubMed
Romero 2011 {published data only}
-
- Romero J, Makani H, Kahan J, Wever‐Pinzon O, Colaco C, Messerli FH. Hyperkalemia with aldosterone antagonist monotherapy in essential hypertension. A meta‐analysis. Journal of Clinical Hypertension 2011;1:A65‐A66. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2011.00459.x] - DOI
Roush 2016 {published data only}
-
- Roush GC, Ernst ME, Kostis JB, Yeasmin S, Sica DA. Dose doubling, relative potency, and dose equivalence of potassium‐sparing diuretics affecting blood pressure and serum potassium: systematic review and meta‐analyses. Journal of Hypertension 2016;34(1):11‐9. [DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000762] - DOI - PubMed
Schmidt 2009 {published data only}
-
- Schmidt BM, Raff U, Schwab J, Bar I, Schmieder RE. MR blockade improves cardiac and vascular target organ damage independent of blood pressure in resistant hypertension [Abstract]. Hypertension 2009;54(4):e37. [DOI: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000359702.48610.72] - DOI
Stier 2003 {published data only}
-
- Stier CT Jr. Eplerenone: a selective aldosterone blocker. Cardiovascular Drug Review 2003;21(3):169‐84. - PubMed
Struthers 2008 {published data only}
Stults 2006 {published data only}
-
- Stults B, Jones RE. Management of hypertension in diabetes. Diabetes Spectrum 2006;19(1):25‐31. [DOI: 10.2337/diaspect.19.1.25] - DOI
Tomaschitz 2012 {published data only}
-
- Tomaschitz A, Fahrleitner‐Pammer A, Pieske B, Verheyen N, Amrein K, Ritz E, et al. Effect of eplerenone on parathyroid hormone levels in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. BMC Endocrine Disorders 2012;12:19. [DOI: 10.1186/1472-6823-12-19] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Toto 2010 {published data only}
Trial 015 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. Clinical review: detailed study reviews section. Drug approvals and databases.
Van Zwieten 2001 {published data only}
-
- Zwieten PA. Drug treatment of isolated systolic hypertension. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2001;16(6):1095‐7. - PubMed
Weber 2002 {published data only}
-
- Weber MA. Clinical implications of aldosterone blockade. American Heart Journal 2002;144(5 Suppl):S12‐S18. - PubMed
Wenger 2008 {published data only}
White 2010 {published data only}
-
- White WB, Calhoun DA, Krum H, Guo W, Trapani AJ, Lefkowitz H, et al. Blockade of aldosterone production as a novel approach to the management of high blood pressure: efficacy and tolerability of the aldosterone synthase inhibitor LCI699 in patients with stage 1‐2 hypertension [Abstract]. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2010;55(10 Suppl 1):A61.E582. [DOI: 10.1016/S0735-1097%2810%2960583-9] - DOI
Yoo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yoo JK, Hwang MH, Luttrell MJ, Cernosek MM, Meade TH, English MW, et al. Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade does not affect arterial compliance in middle‐aged and older adults with and without metabolic syndrome. FASEB Journal 2011;25(1 Suppl):lb480.
Additional references
Arguedas 2009
Banach 2014
Batterink 2010
CHEP 2015
-
- Canadian Hypertension Education Program (CHEP). The 2015 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for blood pressure measurement, diagnosis, assessment of risk, prevention, and treatment of hypertension. Canadian Journal of Cardiology 2015;31:549‐68. - PubMed
Diao 2014
DiPiro 2014
-
- DiPiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, Matzke GR, Wells BG, Posey LM. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach. 9th Edition. New York: McGraw‐Hill Education, 2014.
eCPS 2014
-
- Inspra. Compendium of pharmaceuticals and specialties, online version (e‐CPS). www.e‐therapeutics.ca/cps.select.preliminaryFilter.action?simplePreliminaryFil... (accessed 10 June 2014).
Heran 2009
Jansen 2009
-
- Jansen PM, Danser AHJ, Imholz BP, Meiracker AH. Aldosterone‐receptor antagonism in hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 2009;27:680‐91. - PubMed
JNC 7
Katzung 2012
-
- Katzung BG, Masters SB, Trevor AJ. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. 12th Edition. The McGraw‐Hill Companies, 2012.
Lewington 2002
-
- Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R, Prospective Studies Collaboration. Age‐specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: A meta‐analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 2002;360(9349):1903‐13 [Erratum in: Lancet. 2003 Mar 22;361(9362):1060]. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11911-8] - DOI - PubMed
Muldowney 2009
Musini 2009
NCGC 2011
-
- National Clinical Guideline Centre (UK). Hypertension: The Clinical Management of Primary Hypertension in Adults. London: Royal College of Physicians, 2011.
Van Bemmel 2006
-
- Bemmel T, Gussekloo J, Westendorp RG, Blauw GJ. In a population‐based prospective study, no association between high blood pressure and mortality after age 85 years. Journal of Hypertension 2006;24(2):287‐92. [PUBMED: 16508574] - PubMed
Weber 2014
-
- Weber MA, Schiffrin EL, White WB, Mann S, Lindholm LH, Kenerson JG, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of hypertension in the community a statement by the American Society of Hypertension and the International Society of Hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 2014;32(1):3‐15. [PUBMED: 24270181] - PubMed
Wiysonge 2017
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

