Anti-inflammatory coumarins from Paramignya trimera
- PMID: 28245363
- PMCID: PMC6130569
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2017.1296001
Anti-inflammatory coumarins from Paramignya trimera
Abstract
Context: Paramignya trimera (Oliv.) Burkill (Rutaceae) has been used to treat liver diseases and cancer. However, the anti-inflammatory effects of this medicinal plant and its components have not been elucidated.
Objective: This study investigated chemical constituents of the P. trimera stems and evaluated anti-inflammatory effects of isolated compounds.
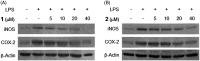
Materials and methods: Cytotoxicity of isolated compounds (5-40 μM) toward BV2 cells was tested using 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) for 24 h. Inhibitory effects of isolated compounds (5-40 μM) on nitrite and PGE2 concentrations were determined using Griess reaction and PGE2 ELISA kit, respectively (pretreated with the compounds for 3 h and then stimulated for 18 h with LPS). Inhibitory effects of compounds (5-40 μM) on iNOS and COX-2 protein expression were evaluated by Western blot analysis (pretreated with the compounds for 3 h and then stimulated for 24 h with LPS).
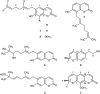
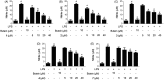
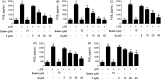
Results: Seven coumarins were isolated and identified as: ostruthin (1), ninhvanin (2), 8-geranyl-7-hydroxycoumarin (3), 6-(6',7'-dihydroxy-3',7'-dimethylocta-2'-enyl)-7-hydroxycoumarin (4), 6-(7-hydroperoxy-3,7-dimethylocta-2,5-dienyl)-7-hydroxycoumarin (5), 6-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,2-dimethyl-2H-1-benzopyran (6), and luvangetin (7). Compounds 1-4 and 7 inhibited NO and PGE2 production in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells, with IC50 values ranging from 9.8 to 46.8 and from 9.4 to 52.8 μM, respectively. Ostruthin (1) and ninhvanin (2) were shown to suppress LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 protein expression.
Discussion and conclusion: The present study provides a scientific rationale for the use of P. trimera in the prevention and treatment of neuroinflammatory diseases. Ostruthin and ninhvanin might have potential therapeutic effects and should be considered for further development as new anti-neuroinflammatory agents.
Keywords: 6-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,2-dimethyl-2H-1-benzopyran; 6-(6′,7′-dihydroxy-3′,7′-dimethylocta-2′-enyl)-7-hydroxycoumarin; 6-(7-hydroperoxy-3,7-dimethylocta-2,5-dienyl)-7-hydroxycoumarin; 8-geranyl-7-hydroxycoumarin; BV2 microglia; Rutaceae; luvangetin; ninhvanin; ostruthin.
Figures
References
-
- Berridge MV, Tan AS.. 1993. Characterization of the cellular reduction of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT): subcellular localization, substrate dependence, and involvement of mitochondrial electron transport in MTT reduction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 303:474–482. - PubMed
-
- Brown GC, Neher JJ.. 2010. Inflammatory neurodegeneration and mechanisms of microglial killing of neurons. Mol Neurobiol. 41:242–247. - PubMed
-
- Chun J, Choi RJ, Khan S, Lee DS, Kim YC, Nam YJ, Lee DU, Kim YS.. 2012. Alantolactone suppresses inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by down-regulating NF-κB, MAPK and AP-1 via the MyD88 signaling pathway in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 14:375–383. - PubMed
-
- Cuong NM, Duc HV, Tai NV, Khanh PN, Ha VT, Huong TT, Nhat ND.. 2013. Initial research on chemical composition of Paramignya trimera. Tap Chi Hoa Hoc. 51:292–296.
-
- Cuong NM, Huong TT, Khanh PN, Tai NV, Ha VT, Son NT, Tai BH, Kim YH.. 2015. Paratrimerins A and B, two new dimeric monoterpene-linked coumarin glycosides from the roots and stems of Paramignya trimera. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 63:945–949. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
